Page 11 - IJB-9-2
P. 11
International Journal of Bioprinting Extrusion-based biomaterial inks
commonly used biomaterial inks superiority by functional bionic bioactivity of extrusion-based biomaterial ink
classification as bioactive materials, mechanical support (Scheme 1).
materials, and rheological additives. The extrusion-based
biomaterial inks are accurately designed by the biological 2.1. Biocompatibility
and chemical modification and pre-gel formation to Biocompatibility is one of the most basic properties of
eventually achieve the balance between biocompatibility, biomaterial ink. Biomaterial ink must be safe to use in
mechanical property and printability, and a preferentially the presence of endogenous tissues of the host in order
selected strategy is conceived by varying the extrusion to avoid immunological rejection or toxic effects. Ideally,
strategies of single-nozzle, co-axial, and multiple-nozzle the implant materials should perform biological functions
extrusion-based bioprinting. Finally, the challenges and and passively or actively produce the desired effects.
prospects of extrudable biomaterial inks, mainly in the Biocompatibility is reflected in the positive and controllable
aspects of organ specificity, tissue elasticity and construct role of biomaterials in the biological safety and function of
microporosity, are elaborated. constructed 3D organisms. Biomaterials can support proper
cell activity and promote molecular signaling or mechanical
2. Properties stimulation, which are critical to the success and function
of transplantation. The biocompatibility of biomaterial inks
Biomaterial ink is a curable material that seeding cells in bioprinting 3D constructs is mainly reflected in the non-
within or on the constructed 3D scaffold. Biocompatibility toxic effect of maintaining or enhancing cell proliferation
and mechanical property are its basic performance and activity in in vitro drug screening application.
requirements. Extrusion-based biomaterial ink needs
the continuous deposition of extruded filaments through 2.2. Degradability
a suitable crosslinking mechanism. Certain swelling Biomaterial ink scaffolds in bioprinted 3D tissue
performance and short-term stability are also very critical constructs will be gradually degraded by the proteases or
to ensure the porosity and integrity of the constructed 3D other degrading substances and replaced by the new ECM
structures. Furthermore, printed biomaterial inks that produced by cells. The degradation rate of biomaterials
are mixed with living cells also require biological activity, needs to match the rate of cell proliferation and new
molecular permeability and printability to ensure the ECM supplementation to ensure constant and steady
delivery of nutrients and the adhesion and growth of cells. substitution of ECM. The slow degradation rate increases
The cell-laden biomaterial inks provide structural support the window period of potential foreign-body reaction or
and allow transmission of signal molecule, cell adhesion, immune response, and creates a host tissue interface. The
differentiation, and proliferation within the biomimetic degradation products of biomaterials also need to be non-
ECM. This section introduces the biocompatibility, toxic and biocompatible with cells or host, as well as can
degradability, mechanical strength, printability, be metabolized and quickly removed from the body. The
solidification formability, molecular permeability, and fast degradation rate may affect the mechanical stability
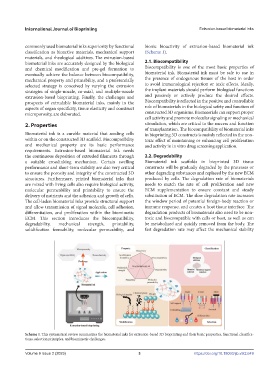
Scheme 1. This systematical review summarizes the biomaterial inks for extrusion-based 3D bioprinting and their basic properties, functional classifica-
tions, selection principles, and biomimetic challenges.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.649