Page 20 - IJB-9-2
P. 20
International Journal of Bioprinting Extrusion-based biomaterial inks
affected by β-sheet structure. Blends of hydroxy propyl temperature-sensitive and reversible gelation. Pluronic can
methyl cellulose of methacrylation and silk fibroin formed be used to construct a mold loaded with matrix gel [157] or a
double network hydrogel, and the fracture strength, vascular network channel in a 3D structure [9,106,108] .
breaking elongation, and compressive reproducibility of
printed constructs increased significantly . Silk fibroin 3.2.8. PEG
[67]
solution is also used in freeform fabrication with nanoclay PEG is often used as pharmaceutic adjuvant. PEG-
and PEG support bath . Bioprinting of silk fibroin is based gels can be formed by physical or covalent
[66]
[158]
more widely used in cartilage tissue engineering. crosslinking, and used internally with FDA approval .
PEGDA is an acrylated derivative of PEG, which can be
3.2.6. Agrose photopolymerized to form a gel with superior mechanical
Agrose, a natural polysaccharide, is obtained from the properties. PEGDA can be easily used to construct 3D
cell walls of red algae. Agarose solution has a sol–gel scaffolds in extrusion-based bioprinting. Similar with
transition in the range from 32°C to 47°C, depending on Pluronic, synthetic polymer chains do not contain
the concentration, and physically polymerizes to form a attachment points that enable interactions with cells,
gel within seconds . Although agrose hydrogels lack cell resulting in a lack of biological activity. Therefore, PEG-
[40]
binding sites and thus have limited bioactivity [153] , adding based gels are generally not printed with cells together
agrose into other polymers can improve print fidelity and because the cells cannot easily migrate and proliferate on
stability of printed structure [40,79] . Agrose can also be used the printed PEGDA scaffolds ; therefore, they are more
[16]
as sacrificial material to construct hollow channel [81,154] . likely to be used as carriers for loading bioactive materials
Besides, agrose can also serve as suspending hydrogel for to improve mechanical strength for maintaining the 3D
the freeform fabrication [155] . structure [103] . Another method to improve the bioactivity
of PEG is peptide modification. For example, PEG-based
3.2.7. Pluronic microgels were modified with the cell adhesive peptide and
Pluronic is a non-ionic triblock copolymer composed then printed together with human mesenchymal stem cells
of polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene-polyoxyethylene. to form 3D constructs, which support cell spreading and
Due to the amphiphilicity caused by the hydrophobicity proliferation [101] .
of polyoxypropylene and the hydrophilicity of
polyoxyethylene, it can form soluble micelles as a carrier 3.2.9. Thermoplastic polymer
of nano drugs for drug delivery. Pluronic is a temperature- PCL, PLA, and PLGA are all thermoplastic polymers,
sensitive polymer and its critical micelle temperature is which could serve as structural materials and are capable of
between 22°C and 37°C. It will self-associate and appear resisting mechanical forces in hybrid constructs, as shown
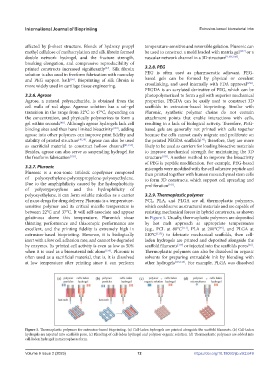
gelatinous above this temperature. Pluronic’s shear in Figure 5. Usually, thermoplastic polymers are deposited
thinning performance and thixotropic performance are by hot melt approach at appropriate temperatures
excellent, and the printing fidelity is extremely high in (e.g., PCL at 80°C [111] , PLA at 200°C , and PLGA at
[45]
extrusion-based bioprinting. However, it is biologically 110°C [117] ) to fabricate mechanical scaffolds, then cell-
inert with a low cell adhesion rate, and cannot be degraded laden hydrogels are printed and deposited alongside the
by enzymes. Its printed cell activity is even as low as 50% scaffold filaments [117] or injected into the scaffolds pores .
[45]
when it is used as a biomaterial ink alone [156] . Pluronic is Thermoplastic polymers can also be dissolved in organic
often used as a sacrificial material, that is, it is dissolved solvents for preparing extrudable ink by blending with
at low temperature after printing since it can perform other hydrogels [115,116] . For example, PLGA was dissolved
Figure 5. Thermoplastic polymers for extrusion-based bioprinting. (a) Cell-laden hydrogels are printed alongside the scaffold filaments. (b) Cell-laden
hydrogels are injected into scaffolds pore. (c) Blending of cell-laden hydrogel and polymer organic solution. (d) Thermoplastic polymers are added into
cell-laden hydrogel in microspheres form.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 12 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.649