Page 17 - IJB-9-2
P. 17
International Journal of Bioprinting Extrusion-based biomaterial inks
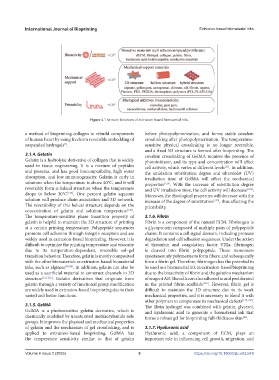
Figure 4. The main functions of extrusion-based biomaterial inks.
a method of bioprinting collagen to rebuild components before photopolymerization, and forms stable covalent
of human heart by using freeform reversible embedding of crosslinking after photopolymerization. The temperature-
suspended hydrogels . sensitive physical crosslinking is no longer reversible,
[5]
and a fixed 3D structure is formed after bioprinting. The
3.1.4. Gelatin covalent crosslinking of GelMA requires the presence of
Gelatin is a hydrolytic derivative of collagen that is widely photoinitiator, and its type and concentration will affect
used in tissue engineering. It is a mixture of peptides cell activity, which varies at different levels . In addition,
[13]
and proteins, and has good biocompatibility, high water the amidation substitution degree and ultraviolet (UV)
absorption, and low immunogenicity. Gelatin is curly in irradiation time of GelMA will affect the mechanical
solutions when the temperature is above 40°C, and it will properties [133] . With the increase of substitution degree
reversibly form α-helical structure when the temperature and UV irradiation time, the cell activity will decrease [134] ;
drops to below 30°C [129] . One percent gelatin aqueous Moreover, the rheological properties will decrease with the
solution will produce chain association and 3D network. increase of the degree of substitution [135] , thus affecting the
The reversibility of this helical structure depends on the printability.
concentration of gelatin and solution temperature [130] .
The temperature-sensitive phase transition property of 3.1.6. Fibrin
gelatin is helpful to maintain the 3D structure of printing Fibrin is a component of the natural ECM. Fibrinogen is
at a certain printing temperature. Polypeptide sequences a glycoprotein composed of multiple pairs of polypeptide
promote cell adhesion through integrin receptors and are chains. It contains a cell signal domain, including protease
widely used in extrusion-based bioprinting. However, it is degradation and cell adhesion sequences. Under the action
difficult to optimize the printing temperature and viscosity of thrombin and coagulation factor VIIIa, fibrinogen
due to its temperature-dependent, reversible sol–gel is cleaved into fibrin polypeptide. These monomers
transition behavior. Therefore, gelatin is mostly composited spontaneously polymerize to form fibers, and subsequently
with the other biomaterials as extrusion-based biomaterial form a fibrin gel. Therefore, fibrinogen has the potential to
inks, such as alginate [87,88] . In addition, gelatin can also be be used as a biomaterial ink in extrusion-based bioprinting
used as a sacrificial material to construct channels in 3D due to the bioactivity of fibrin and the gelation mechanism
structure [131,132] . Gelatin derivatives that originate from of reagent AB. The cells can also adhered to and proliferated
gelatin through a variety of functional group modification in the printed fibrin scaffolds [136] . However, fibrin gel is
are widely used in extrusion-based bioprinting due to their difficult to maintain the 3D structure due to its weak
varied and better functions. mechanical properties, and it is necessary to blend it with
other polymers to compensate its mechanical defects [137,138] .
3.1.5. GelMA The fibrin hydrogel was combined with gelatin, glycerol,
GelMA is a photosensitive gelatin derivative, which is and hyaluronic acid to generate a biomaterial ink that
chemically modified by unsaturated methacrylamide side forms a robust gel for bioprinting full-thickness skin .
[46]
groups. It improves the physical and mechanical properties
of gelatin and the mechanism of gel crosslinking, and is 3.1.7. Hyaluronic acid
applied to extrusion-based bioprinting. GelMA has Hyaluronic acid, a component of ECM, plays an
the temperature sensitivity similar to that of gelatin important role in influencing cell growth, migration, and
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i2.649