Page 433 - IJB-9-3
P. 433
International Journal of Bioprinting Gelatin-PVA crosslinked genipin bioinks for skin tissue engineering
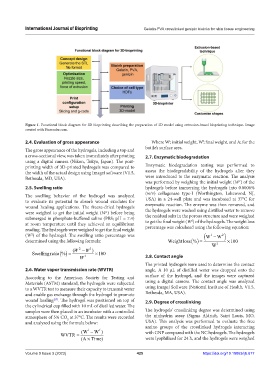
Figure 1. Functional block diagram for 3D bioprinting describing the preparation of 3D model using extrusion-based bioprinting technique. Image
created with Biorender.com.
2.4. Evaluation of gross appearance Where W; initial weight, W; final weight, and A; for the
i
f
The gross appearance of the hydrogels, including a top and bottle’s surface area.
a cross-sectional view, was taken immediately after printing 2.7. Enzymatic biodegradation
using a digital camera (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The post-
printing width of 3D-printed hydrogels was compared to Enzymatic biodegradation testing was performed to
the width of the actual design using ImageJ software (V1.5, assess the biodegradability of the hydrogels after they
Bethesda, MD, USA). were introduced to the enzymatic reaction. The analysis
was performed by weighing the initial weight (W ) of the
1
2.5. Swelling ratio hydrogels before immersing the hydrogels into 0.0006%
The swelling behavior of the hydrogel was analyzed (w/v) collagenase type-I (Worthington, Lakewood, NJ,
to evaluate its potential to absorb wound exudates for USA) in a 24-well plate and was incubated at 37°C for
wound healing applications. The freeze-dried hydrogels enzymatic reaction. The enzyme was then removed, and
were weighed to get the initial weight (W ) before being the hydrogels were washed using distilled water to remove
1
submerged in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH = 7.4) the residual salts in the porous structure and were weighed
2
at room temperature until they achieved an equilibrium to get the final weight (W ) of the hydrogels. The weight loss
reading. The hydrogels were weighed to get the final weight percentage was calculated using the following equation:
(W ) of the hydrogel. The swelling ratio percentage was W ( 1 − W )
2
2
determined using the following formula: Weight loss % () = ×100
W 1
(W − W 1 )
2
Swellingratio % () = ×100
W 1 2.8. Contact angle
The printed hydrogels were used to determine the contact
2.6. Water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) angle. A 10 µL of distilled water was dropped onto the
According to the American Society for Testing and surface of the hydrogel, and the images were captured
Materials (ASTM) standard, the hydrogels were subjected using a digital camera. The contact angle was analyzed
to a WVTR test to measure their capacity to transmit water using ImageJ Software (National Institute of Health, V1.5,
and enable gas exchange through the hydrogel to promote Bethesda, MA, USA).
wound healing . The hydrogel was positioned on top of 2.9. Degree of crosslinking
[27]
the cylindrical cup filled with 10 mL of distilled water. The
samples were then placed in an incubator with a controlled The hydrogels’ crosslinking degree was determined using
atmosphere of 5% CO at 37°C. The results were recorded the ninhydrin assay (Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO,
2
and analyzed using the formula below: USA). This analysis was performed to evaluate the free
amino groups of the crosslinked hydrogels interacting
f
i
WVTR = ( W − W ) with GNP compared with the NC hydrogels. The hydrogels
( ATime× ) were lyophilized for 24 h, and the hydrogels were weighed
Volume 9 Issue 3 (2023) 425 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.677