Page 338 - IJB-9-5
P. 338
International Journal of Bioprinting Review of 4D-printed smart medical implants
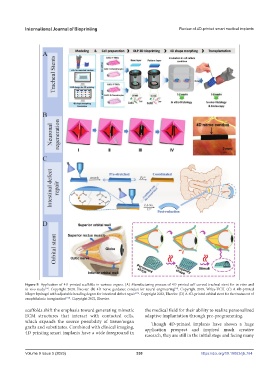
Figure 9. Application of 4D-printed scaffolds in various organs. (A) Manufacturing process of 4D-printed self-curved tracheal stent for in vitro and
in vivo study . Copyright 2020, Elsevier. (B) 4D nerve guidance conduit for neural engineering . Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (C) A 4D-printed
[76]
[33]
bilayer hydrogel with adjustable bending degree for intestinal defect repair . Copyright 2022, Elsevier. (D) A 4D-printed orbital stent for the treatment of
[85]
enophthalmic invagination [153] . Copyright 2022, Elsevier.
scaffolds shift the emphasis toward generating mimetic the medical field for their ability to realize personalized
ECM structures that interact with contacted cells, adaptive implantation through pre-programming.
which expands the source possibility of tissue/organ Though 4D-printed implants have shown a huge
grafts and substitutes. Combined with clinical imaging, application prospect and inspired much creative
4D printing smart implants have a wide foreground in
research, they are still in the initial stage and facing many
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 330 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.764