Page 469 - IJB-9-5
P. 469
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D printed hydrogel for infected wound healing via PDT
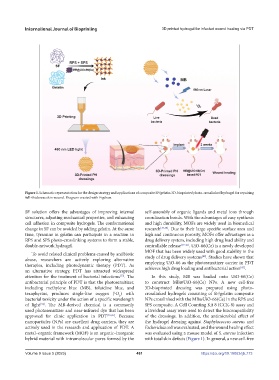
Figure 1. Schematic representation for the design strategy and applications of composite SF/gelatin 3D-bioprinted photo-crosslinked hydrogel for repairing
full-thickness skin wound. Diagram created with Figdraw.
SF solution offers the advantages of improving internal self-assembly of organic ligands and metal ions through
structures, adjusting mechanical properties, and enhancing coordination bonds. With the advantages of easy synthesis
cell adhesion in composite hydrogels. The conformational and high durability, MOFs are widely used in biomedical
change in SF can be avoided by adding gelatin. At the same research [37,38] . Due to their large specific surface area and
time, tyramine in gelatin can participate in a reaction in high and continuous porosity, MOFs offer advantages as a
RPS and SPS photo-crosslinking systems to form a stable, drug delivery system, including high drug load ability and
double-network hydrogel. controllable release [39-41] . UiO-66(Ce) is a newly developed
MOF that has been widely used with good stability in the
To avoid related clinical problems caused by antibiotic [42]
abuse, researchers are actively exploring alternative study of drug delivery systems . Studies have shown that
employing UiO-66 as the photosensitizer carrier in PDT
therapies, including photodynamic therapy (PDT). As achieves high drug loading and antibacterial action .
[43]
an alternative strategy, PDT has attracted widespread
attention for the treatment of bacterial infections . The In this study, MB was loaded onto UiO-66(Ce)
[33]
antibacterial principle of PDT is that the photosensitizer, to construct MB@UiO-66(Ce) NPs. A new cell-free
including methylene blue (MB), toluidine blue, and 3D-bioprinted dressing was prepared using photo-
texaphyrins, produces single-line oxygen ( O ) with crosslinked hydrogels consisting of SF/gelatin composite
1
2
bacterial toxicity under the action of a specific wavelength NPs crosslinked with the MB@UiO-66(Ce) in the RPS and
of light . The MB-derived chemical is a commonly SPS composite. A Cell Counting Kit 8 (CCK-8) assay and
[34]
used photosensitizer and near-infrared dye that has been a live/dead assay were used to detect the biocompatibility
approved for clinic application in PDT [35,36] . Because of the dressings. In addition, the antimicrobial effect of
nanoparticles (NPs) are excellent drug carriers, they are the hydrogel dressing against Staphylococcus aureus and
actively used in the research and application of PDT. A Escherichia coli was evaluated, and the wound healing effect
metal–organic framework (MOF) is an organic–inorganic was evaluated using a mouse model of S. aureus infection
hybrid material with intramolecular pores formed by the with total skin defects (Figure 1). In general, a new cell-free
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 461 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.773