Page 48 - IJB-9-5
P. 48
International Journal of Bioprinting Precise fabrication of engineered vascular networks
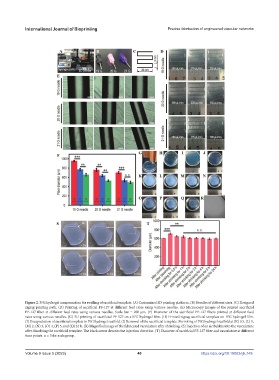
Figure 2. P/G hydrogel compensation for swelling of sacrificial template. (A) Customized 3D printing platform. (B) Needles of different sizes. (C) Designed
zigzag printing path. (D) Printing of sacrificial PF-127 at different feed rates using various needles. (E) Microscopy images of the printed sacrificial
PF-127 fiber at different feed rates using various needles. Scale bar = 200 μm. (F) Diameter of the sacrificial PF-127 fibers printed at different feed
rates using various needles. (G) 3D printing of sacrificial PF-127 on a P/G hydrogel film. (H) Printed zigzag sacrificial template on P/G hydrogel film.
(I) Encapsulation of sacrificial template in P/G hydrogel scaffold. (J) Removal of the sacrificial template. Shrinking of P/G hydrogel scaffold at (K) 0.5, (L) 1,
(M) 2, (N) 3, (O) 4, (P) 5, and (Q) 24 h. (R) Magnified image of the fabricated vasculature after shrinking. (S) Injection of an air bubble into the vasculature
after dissolving the sacrificial template. The black arrow denotes the injection direction. (T) Diameter of sacrificial PF-127 fiber and vasculature at different
time points. n = 3 for each group.
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 40 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.749