Page 53 - IJB-9-5
P. 53
International Journal of Bioprinting Precise fabrication of engineered vascular networks
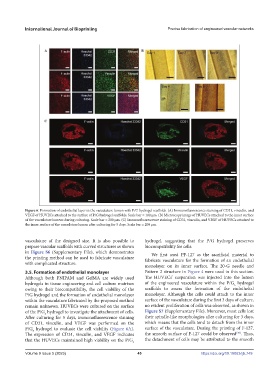
Figure 6. Formation of endothelial layer in the vasculature lumen with P/G hydrogel scaffolds. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of CD31, vinculin, and
VEGF of HUVECs attached to the surface of P/G hydrogel scaffolds. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Microscopy image of HUVECs attached to the inner surface
of the vasculature lumens during culturing. Scale bar = 200 μm. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of CD31, vinculin, and VEGF of HUVECs attached to
the inner surface of the vasculature lumen after culturing for 5 days. Scale bar = 200 μm.
vasculature of the designed size. It is also possible to hydrogel, suggesting that the P/G hydrogel preserves
prepare vascular scaffolds with curved structures as shown biocompatibility for cells.
in Figure S6 (Supplementary File), which demonstrates We first used PF-127 as the sacrificial material to
the printing method can be used to fabricate vasculature fabricate vasculature for the formation of an endothelial
with complicated structure.
monolayer on its inner surface. The 20-G needle and
3.5. Formation of endothelial monolayer Pattern 2 structure in Figure 4 were used in this section.
Although both PNIPAM and GelMA are widely used The HUVECs’ suspension was injected into the lumen
hydrogels in tissue engineering and cell culture matrixes of the engineered vasculature within the P/G hydrogel
3
owing to their biocompatibility, the cell viability of the scaffolds to assess the formation of the endothelial
P/G hydrogel and the formation of endothelial monolayer monolayer. Although the cells could attach to the inner
within the vasculature fabricated by the proposed method surface of the vasculature during the first 3 days of culture,
remain unknown. HUVECs were cultured on the surface no evident proliferation of cells was observed, as shown in
of the P/G hydrogel to investigate the attachment of cells. Figure S7 (Supplementary File). Moreover, most cells lost
3
After culturing for 5 days, immunofluorescence staining their spindle-like morphologies after culturing for 3 days,
of CD31, vinculin, and VEGF was performed on the which means that the cells tend to detach from the inner
P/G hydrogel to evaluate the cell viability (Figure 6A). surface of the vasculature. During the printing of F-127,
3
[39]
The expression of CD31, vinculin, and VEGF indicates the smooth surface of F-127 could be observed . Thus,
that the HUVECs maintained high viability on the P/G the detachment of cells may be attributed to the smooth
3
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 45 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.749