Page 56 - IJB-9-5
P. 56
International Journal of Bioprinting Precise fabrication of engineered vascular networks
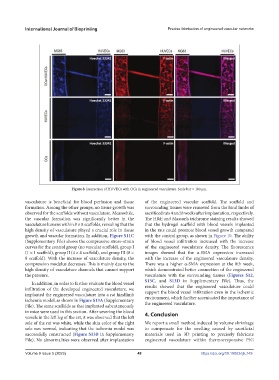
Figure 8. Interaction of HUVECs with OCs in engineered vasculature. Scale bar = 100 μm.
vasculature is beneficial for blood perfusion and tissue of the engineered vascular scaffold. The scaffold and
formation. Among the other groups, no tissue growth was surrounding tissues were removed from the hind limbs of
observed for the scaffolds without vasculature. Meanwhile, sacrificed rats 4 and 8 weeks after implantation, respectively.
the vascular formation was significantly better in the The H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining results showed
vasculature lumens within 8 × 8 scaffolds, revealing that the that the hydrogel scaffold with blood vessels implanted
high density of vasculature played a crucial role in tissue in the rats could promote blood vessel growth compared
growth and vascular formation. In addition, Figure S11C with the control group, as shown in Figure 10. The ability
(Supplementary File) shows the compressive stress–strain of blood vessel infiltration increased with the increase
curves for the control group (no vascular scaffold), group I of the engineered vasculature density. The fluorescence
(1 × 1 scaffold), group II (4 × 4 scaffold), and group III (8 × images showed that the α-SMA expression increased
8 scaffold). With the increase of vasculature density, the with the increase of the engineered vasculature density.
compression modulus decreases. This is mainly due to the There was a higher α-SMA expression at the 8th week,
high density of vasculature channels that cannot support which demonstrated better connection of the engineered
the pressure. vasculature with the surrounding tissues (Figures S12,
S13C, and S13D in Supplementary File). Thus, the
In addition, in order to further evaluate the blood vessel
infiltration of the developed engineered vasculature, we results showed that the engineered vasculature could
support the blood vessel infiltration even in the ischemic
implanted the engineered vasculature into a rat hindlimb environment, which further accentuated the importance of
ischemia model, as shown in Figure S13A (Supplementary the engineered vasculature.
File). The same scaffolds as that implanted subcutaneously
in mice were used in this section. After severing the blood 4. Conclusion
vessels in the left leg of the rat, it was observed that the left
sole of the rat was white, while the skin color of the right We report a small method induced by volume shrinkage
sole was normal, indicating that the ischemia model was to compensate for the swelling caused by sacrificial
successfully constructed (Figure S13B in Supplementary materials used in 3D printing to precisely fabricate
File). No abnormalities were observed after implantation engineered vasculature within thermoresponsive P/G
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 48 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.749