Page 57 - IJB-9-5
P. 57
International Journal of Bioprinting Precise fabrication of engineered vascular networks
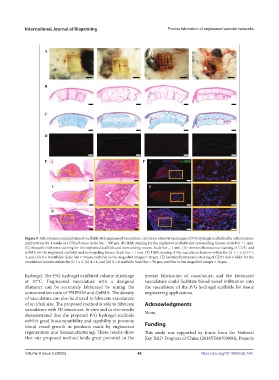
Figure 9. Subcutaneous implantation of scaffolds with engineered vasculature. (A) Gross observation images of P/G hydrogel scaffolds after subcutaneous
implantation for 4 weeks in C57BL/6 mice. Scale bar = 500 μm. (B) H&E staining for the implanted scaffolds and surrounding tissues. Scale bar = 1 mm.
(C) Masson’s trichrome staining for the implanted scaffolds and surrounding tissues. Scale bar = 1 mm. (D) Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 and
α-SMA for the implanted scaffolds and surrounding tissues. Scale bar = 1 mm. (E) H&E staining of the vasculature lumens within the (i) 1 × 1, (ii) 4 ×
4, and (iii) 8 × 8 scaffolds. Scale bar = 50 μm; scale bar in the magnified images = 20 μm. (F) Immunofluorescence staining of CD31 and α-SMA for the
vasculature lumens within the (i) 1 × 1, (ii) 4 × 4, and (iii) 8 × 8 scaffolds. Scale bar = 50 μm; scale bar in the magnified images = 20 μm.
hydrogel. The P/G hydrogel exhibited volume shrinkage precise fabrication of vasculature, and the fabricated
at 37°C. Engineered vasculature with a designed vasculature could facilitate blood vessel infiltration into
diameter can be accurately fabricated by tuning the the vasculature of the P/G hydrogel scaffolds for tissue
concentration ratio of PNIPAM and GelMA. The density engineering applications.
of vasculature can also be altered to fabricate vasculature
of an ideal size. The proposed method is able to fabricate Acknowledgments
vasculature with 3D structures. In vitro and in vivo results
demonstrated that the prepared P/G hydrogel scaffolds None.
exhibit good biocompatibility and capability to promote
blood vessel growth in products made by engineered Funding
regeneration and biomanufacturing. These results show This study was supported by funds from the National
that our proposed method holds great potential in the Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0703000), Projects
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 49 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.749