Page 81 - IJB-9-5
P. 81
International Journal of Bioprinting Biocompatible BSA-GMA and TPP of 3D hydrogels with free radical type I photoinitiator
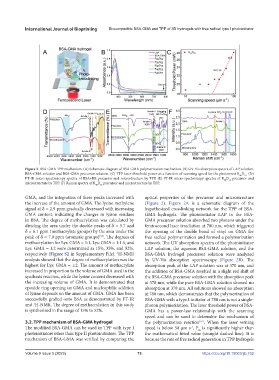
Figure 2. BSA-GMA TPP mechanism. (A) Schematic diagram of BSA-GMA polymerization mechanism. (B) UV-Vis absorption spectra of LAP solution,
BSA-GMA solution and BSA-GMA precursor solution. (C) TPP laser threshold power as a function of scanning speed for the photoresist R D . (D)
40
35
FT-IR micro-spectroscopy spectra of BSA+RB precursor and microstructure by TPP. (E) FT-IR micro-spectroscopy spectra of R D precursor and
40
52
microstructure by TPP. (F) Raman spectra of R D precursor and microstructure by TPP.
52
40
GMA, and the integration of these peaks increased with optical properties of the precursor and microstructure
the increase of the amount of GMA. The lysine methylene (Figure 2). Figure 2A is a schematic diagram of the
signal at δ = 2.9 ppm gradually decreased with increasing hypothesized crosslinking network for the TPP of BSA-
GMA content, indicating the changes in lysine residues GMA hydrogels. The photoinitiator LAP in the BSA-
in BSA. The degree of methacrylation was calculated by GMA precursor solution absorbed two photons under the
dividing the area under the double peaks of δ = 5.7 and femtosecond laser irradiation at 780 nm, which triggered
δ = 6.1 ppm (methacrylate groups) by the area under the the opening of the double bond of vinyl on GMA for
peak of δ = 7.0 ppm (aromatic groups) . The degrees of free radical polymerization and formed a polymerization
[56]
methacrylation for Lys: GMA = 1:1, Lys: GMA = 1:1.5, and network. The UV absorption spectra of the photoinitiator
Lys: GMA = 1:2 were determined as 15%, 35%, and 52%, LAP solution, the aqueous BSA-GMA solution, and the
respectively (Figure S2 in Supplementary File). H-NMR BSA-GMA hydrogel precursor solution were analyzed
1
analysis showed that the degree of methacrylation was the by UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy (Figure 2B). The
highest for Lys: GMA = 1:2. The amount of methacrylate absorption peak of the LAP solution was at 370 nm, and
increased in proportion to the volume of GMA used in the the addition of BSA-GMA resulted in a slight red shift of
synthesis reaction, while the lysine content decreased with the BSA-GMA precursor solution with the absorption peak
the increasing volume of GMA. It is demonstrated that at 378 nm, while the pure BSA-GMA solution showed no
epoxide ring opening on GMA and nucleophilic addition absorption at 378 nm. All solutions showed no absorption
of lysine depends on the amount of GMA. GMA has been at 780 nm, which demonstrates that the polymerization of
successfully grafted onto BSA as demonstrated by FT-IR BSA-GMA with a type I initiator at 780 nm is not a single-
and H-NMR. The degree of methacrylation in this study photon polymerization. The laser threshold power of BSA-
1
is synthesized in the range of 15% to 52%. GMA has a power-law relationship with the scanning
speed and can be used to determine the mechanism of
3.2. TPP mechanism of BSA-GMA hydrogel the polymerization reaction . When the laser writing
[57]
The modified BSA-GMA can be used in TPP with type I speed is below 50 μm s , P is significantly higher than
-1
th
photoinitiators other than type II photoinitiators. The TPP the mathematical fitted value (straight dashed line). It is
mechanism of BSA-GMA was verified by comparing the because the rate of free radical generation in TPP hydrogels
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 73 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.752