Page 86 - IJB-9-5
P. 86
International Journal of Bioprinting Biocompatible BSA-GMA and TPP of 3D hydrogels with free radical type I photoinitiator
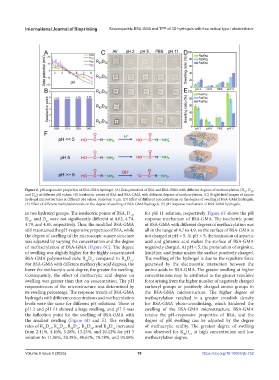
Figure 6. pH-responsive properties of BSA-GMA hydrogel. (A) Zeta potentials of BSA and BSA-GMA with different degrees of methacrylation (D , D ,
35
15
and D ) at different pH values. (B) Isoelectric points of BSA and BSA-GMA with different degrees of methacrylation. (C) Bright-field images of square
52
hydrogel microstructures at different pH values. Scale bar: 5 μm. (D) Effect of different concentrations on the degree of swelling of BSA-GMA hydrogels.
(E) Effect of different methylation levels on the degree of swelling of BSA-GMA hydrogels. (F) pH response mechanism of BSA-GMA hydrogels.
in two hydroxyl groups. The isoelectric points of BSA, D , for pH 11 solution, respectively. Figure 6F shows the pH
15
D , and D were not significantly different at 4.62, 4.74, response mechanism of BSA-GMA. The isoelectric point
35
52
4.79, and 4.85, respectively. Thus, the modified BSA-GMA of BSA-GMA with different degrees of methacrylation was
still maintained the pH-responsive properties of BSA, while all in the range of 4.7 to 4.9, so the surface of BSA-GMA is
the degree of swelling of the microscopic square structure not charged at pH = 5. At pH > 5, the ionization of aspartic
was adjusted by varying the concentration and the degree acid and glutamic acid makes the surface of BSA-GMA
of methacrylation of BSA-GMA (Figure 6C). The degree negatively charged. At pH < 5, the protonation of arginine,
of swelling was slightly higher for the highly concentrated histidine, and lysine makes the surface positively charged.
BSA-GMA polymerized cube R D compared to R D . The swelling of the hydrogel is due to the repulsive force
52
52
20
40
For BSA-GMA with different methacrylic acid degrees, the generated by the electrostatic interaction between the
lower the methacrylic acid degree, the greater the swelling. amino acids in BSA-GMA. The greater swelling at higher
Consequently, the effect of methacrylic acid degree on concentrations may be attributed to the greater repulsive
swelling was greater than that on concentration. The pH force arising from the higher number of negatively charged
responsiveness of the microstructure was determined by carboxyl groups or positively charged amino groups in
its swelling percentage. The response trends of BSA-GMA the BSA-GMA microstructure. The higher degree of
hydrogels with different concentrations and methacrylation methacrylation resulted in a greater crosslink density
levels were the same for different pH solutions. Those at for BSA-GMA photo-crosslinking, which hindered the
pH 2 and pH 11 showed a large swelling, and pH 5 was swelling of the BSA-GMA microstructure. BSA-GMA
the inflection point for the swelling of BSA-GMA with retains the pH-responsive properties of BSA, and the
the smallest swelling (Figure 6D and E). The swelling degree of pH swelling can be adjusted by the degree
rates of R D , R D , R D , R D , and R D increased of methacrylic acidity. The greatest degree of swelling
40
52
20
15
35
40
52
52
30
40
from 2.41%, 4.16%, 5.28%, 13.25%, and 20.12% for pH 5 was observed for R D at high concentration and low
15
40
solution to 11.96%, 28.38%, 40.67%, 78.78%, and 95.08% methacrylation degree.
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 78 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.752