Page 97 - IJB-9-5
P. 97
International Journal of Bioprinting Application and prospects of 3D printable microgels
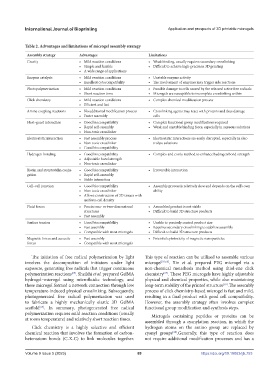
Table 2. Advantages and limitations of microgel assembly strategy
Assembly strategy Advantages Limitations
Gravity • Mild reaction conditions • Weak binding, usually requires secondary crosslinking
• Simple and feasible • Difficult to achieve high-precision 3D printing
• A wide range of applications
Enzyme catalysis • Mild reaction conditions • Unstable enzyme activity
• Excellent cytocompatibility • The involvement of enzymes may trigger side reactions
Photopolymerization • Mild reaction conditions • Possible damage to cells caused by the released active free radicals
• Short reaction time • Microgels are susceptible to incomplete crosslinking within
Click chemistry • Mild reaction conditions • Complex chemical modification process
• Efficient and fast
Amine coupling reactions • No additional modification process • Crosslinking agents may react with proteins and thus damage
• Faster assembly cells
Host–guest interaction • Good biocompatibility • Complex functional group modifications required
• Rapid self-assembly • Weak and unstable binding force, especially in aqueous solutions
• Non-toxic crosslinker
Electrostatic interaction • Fast assembly process • Electrostatic interactions are easily disrupted, especially in elec-
• Non-toxic crosslinker trolyte solutions
• Good biocompatibility
Hydrogen bonding • Good biocompatibility • Complex and costly method to enhance hydrogen bond strength
• Adjustable bond strength
• Non-toxic crosslinker
Biotin and streptavidin conju- • Good biocompatibility • Irreversible interaction
gation • Rapid self-assembly
• Stable interaction
Cell–cell junction • Good biocompatibility • Assembly process is relatively slow and depends on the cell’s own
• Non-toxic crosslinker ability
• Allows construction of 3D tissues with
uniform cell density
Fluid forces • Precise one- or two-dimensional • Assembled product is not stable
structures • Difficult to build 3D structure products
• Fast assembly
Surface tension • Good biocompatibility • Unable to precisely control product size
• Fast assembly • Requires secondary crosslinking to stabilize assembly
• Compatible with most microgels • Difficult to build 3D structure products
Magnetic forces and acoustic • Fast assembly • Potential cytotoxicity of magnetic nanoparticles
forces • Compatible with most microgels
The initiation of free radical polymerization by light This type of reaction can be utilized to assemble various
involves the decomposition of initiators under light microgel [59,66] . Xin et al. prepared PEG microgel via a
exposure, generating free radicals that trigger continuous non-chemical metathesis method using thiol-ene click
polymerization reactions . Sheikhi et al. prepared GelMA chemistry . These PEG microgels have highly adjustable
[65]
[67]
hydrogel–microgel using microfluidic technology, and physical and chemical properties, while also maintaining
these microgel formed a network connection through low long-term stability of the printed structure .The assembly
[67]
temperature-induced physical crosslinking. Subsequently, process of click chemistry-based microgel is fast and mild,
photogenerated free radical polymerization was used resulting in a final product with good cell compatibility.
to fabricate a highly mechanically elastic 3D GelMA However, the assembly strategy often involves complex
scaffold . In summary, photogenerated free radical functional group modification and synthesis steps.
[65]
polymerization requires mild reaction conditions (usually Microgels containing peptides or proteins can be
at room temperature) and relatively short reaction times.
assembled through a cyanylation reaction, in which the
Click chemistry is a highly selective and efficient hydrogen atoms on the amino group are replaced by
chemical reaction that involves the formation of carbon- cyanyl groups .Generally, this type of reaction does
[68]
heteroatom bonds (C-X-C) to link molecules together. not require additional modification processes and has a
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 89 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.753