Page 99 - IJB-9-5
P. 99
International Journal of Bioprinting Application and prospects of 3D printable microgels
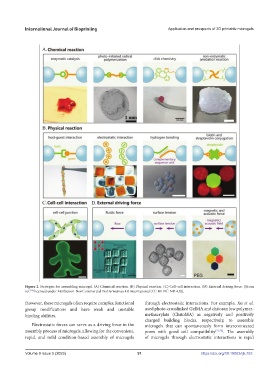
Figure 2. Strategies for assembling microgel. (A) Chemical reaction. (B) Physical reaction. (C) Cell–cell interaction. (D) External driving force. [(from
ref. licensed under Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)].
[28]
However, these microgels often require complex functional through electrostatic interactions. For example, Xu et al.
group modifications and have weak and unstable used photo-crosslinked GelMA and chitosan low polymer-
binding abilities. methacrylate (ChitoMA) as negatively and positively
charged building blocks, respectively, to assemble
Electrostatic forces can serve as a driving force in the microgels that can spontaneously form interconnected
assembly process of microgels, allowing for the convenient, pores with good cell compatibility [71,72] . The assembly
rapid, and mild condition-based assembly of microgels of microgels through electrostatic interactions is rapid
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 91 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.753