Page 494 - IJB-9-6
P. 494
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting cell-laden protein-based hydrogel
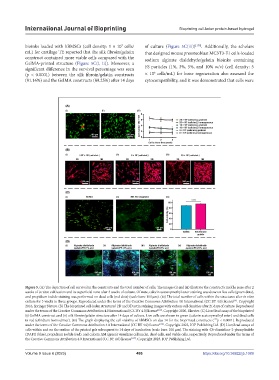
bioinks loaded with hBMSCs (cell density: 1 × 10 cells/ of culture (Figure 5C(iii)) [138] . Additionally, the scholars
7
mL) for cartilage TE reported that the silk fibroin/gelatin that designed mouse preosteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells-loaded
construct contained more viable cells compared with the sodium alginate dialdehyde/gelatin bioinks containing
GelMA-printed structure (Figure 5C(i, ii)). Moreover, a
significant difference in the survival percentage was seen FS particles (1%, 3%, 5%, and 10% w/v) (cell density: 5
6
(p < 0.0001) between the silk fibroin/gelatin constructs × 10 cells/mL) for bone regeneration also assessed the
(91.16%) and the GelMA constructs (89.25%) after 14 days cytocompatibility, and it was demonstrated that cells were
Figure 5. (A) The depiction of cell survival in the constructs and the total number of cells. The images (i) and (ii) illustrate the construct’s middle zone after 2
weeks of in vitro cultivation and its superficial zone after 3 weeks of culture. Of note, calcein acetoxymethyl ester staining was done on live cells (green dots),
and propidium iodide staining was performed on dead cells (red dots) (scale bars: 100 μm). (iii) The total number of cells within the structures after in vitro
culture for 3 weeks in three groups. Reproduced under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license . Copyright
[91]
2016, Springer Nature. (B) The bioprinted cell-laden structures’ 2D and 3D actin staining images with various cell densities after 21 days of culture. Reproduced
under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license [114] . Copyright 2020, Elsevier. (C) Live/dead assay of the bioprinted
(i) GelMA construct and (ii) silk fibroin/gelatin structure after 14 days of culture. Live cells are shown in green (calcein acetoxymethyl ester) and dead cells
in red (ethidium homodimer). (iii) The graph displaying the cell viability of hBMSCs on day 14 for the bioprinted constructs ( p < 0.0001). Reproduced
****
under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license [138] . Copyright 2023, IOP Publishing Ltd. (D) Live/dead assays of
cells within and on the surface of the printed gels subsequent to 14 days of incubation (scale bars: 100 µm). The staining with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
(DAPI) (blue), propidium iodide (red), and calcein AM (green) visualizes cell nuclei, dead cells, and viable cells, respectively. Reproduced under the terms of
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license [137] . Copyright 2023, IOP Publishing Ltd.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 486 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1089