Page 155 - IJOCTA-15-2
P. 155
A. Yoku¸s, H. Durur, M.H. Ekici / IJOCTA, Vol.15, No.2, pp.343-353 (2025)
A higher diffusion coefficient allows matter
or energy to diffuse more rapidly through the
medium. This is especially important in media
where the speed of propagation of the wave is a
significant factor. Different diffusion coefficients
also affect the amount of energy carried by the
wave. A higher diffusion coefficient will distrib-
ute the energy of the wave over a wider area
more quickly, while a lower diffusion coefficient
will cause the energy to remain more localized.
The diffusion coefficient has a significant influence
on the propagation characteristics of the wave.
However, to determine exactly how these effects
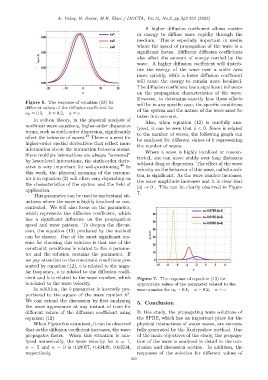
Figure 6. The response of equation (13) for will be in any specific case, the specific conditions
different values of the diffusion coefficient for of the system and the nature of the wave must be
α 0 = 0.5, k = 0.2, a = e
taken into account.
In soliton theory, in the physical analysis of
Also, when equation (12) is carefully ana-
nonlinear wave equations, higher-order dispersion lyzed, it can be seen that `o < 0. Since is related
terms, such as sixth-order dispersion, significantly to the number of waves, the following graph can
affect the behavior of waves. 47 There is a need for
be analyzed for different values of k representing
higher-order spatial derivatives that reflect more
the number of waves.
information about the interaction between atoms. Where a wave is highly localized or concen-
Since multiple interactions are always ”screened” trated, one can move stably over long distances
by lower-level interactions, the sixth-order deriv- without drag or dispersion. The effect of the wave
ative is very important for well-positioning. 49 In velocity on the behavior of this wave, called a soli-
this work, the physical meaning of the parame- ton, is significant. As the wave number increases,
ter `o in equation (2) will often vary depending on the wave amplitude increases and it is clear that
the characteristics of the system and the field of |`o| → 0 . This can be clearly observed in Figure
application. 7.
This parameter can be used to understand sit-
uations where the wave is highly localized or con-
centrated. We will also focus on the parameter,
which represents the diffusion coefficient, which
has a significant influence on the propagation
speed and wave pattern. To deepen the discus-
sion, the equation (13) produced by the method
can be chosen. One of the most significant rea-
sons for choosing this solution is that one of the
constraint conditions is related to the `o parame-
ter and the solution contains the parameter. If
we pay attention to the constraint conditions pre-
sented by equation (12), v is related to the angu-
lar frequency, κ is related to the diffusion coeffi-
cient and k is related to the wave number, which Figure 7. The response of equation (13) for
is related to the wave velocity. appropriate values of the parameter related to the
In addition, the `o parameter is inversely pro- wave number for α 0 = 0.5, κ = 0.2, a = e
2
portional to the square of the wave number k .
We can extend the discussion by first analyzing
5. Conclusion
the wave appearance at any instant of time for
different values of the diffusion coefficient using In this study, the propagating wave solutions of
equation (12). the SPBE, which has an important place for the
When Figure 6 is examined, it can be observed physical interactions of water waves, are success-
that as the diffusion coefficient increases, the wave fully generated by the Kudryashov method. One
propagates faster. When this situation is ana- of the main objectives of the study, the propaga-
lyzed numerically, the wave velocity for κ = 1, tion of the wave is analyzed in detail in the con-
κ = 5 and κ = 9 is 0.29057, 0.49439, 0.63594, clusion and discussion section. In addition, the
respectively. responses of the solution for different values of
350