Page 197 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 197
FastLoader: Leveraging large language models to accelerate cargo loading optimization with numerous
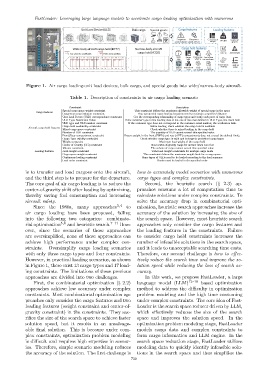
Figure 1. Air cargo loading:unit load devices, bulk cargo, and special goods into wide/narrow-body aircraft.
Table 1. Description of constraints in air cargo loading scenario
Constraint Description
Special cargo space weight constraint This constraint defines the maximum allowable weight of special cargo in the space
Cargo features
Dangerous cargo isolation constraint Any two special cargo loading locations need to maintain a specified distance
Unit Load Device (ULD) correspondence constraint Get the corresponding relationship of cargo types and verify each piece of cargo data
ULD Type Restriction Rules If the container type in the loading data is not one of the ones defined in ULD Type, the check fails
ULD type and ULD number constraint If the container type does not correspond to the container serial number, the verification fails.
Cargo hold availability constraint Before loading, check whether the cargo hold is available
Aircraft cargo hold features
Mixed cargo space constraint Check whether there is mixed loading in the cargo hold
Number of ULD constraint The quantity of ULD cannot exceed this specified value
Front/Rear compartment constraint Ensure weight in the front (FWD) and rear (AFT) compartments does not exceed the defined limits.
Cargo Type validity constraint Check whether cargo type is valid and belongs to predefined cargo types.
Weight constraint Maximum load weight of the cargo hold
Center of Gravity (CG) constraint Ideal center-of-gravity range for airliner when zero fuel
Volume constraint The volume of cargo cannot exceed this specified value
Loading features Joint weight constraint Total load weight constraints for multiple cargo holds
Cargo space weight constraint This constraint defines the maximum weight limit for a cargo space.
Continuous loading constraint Some types of ULDs need to be loaded according to the load sequence
Load order constraint Goods must be loaded in the specified order
is to transfer and load cargoes onto the aircraft, how to accurately model scenarios with numerous
and the third step is to prepare for the departure. cargo types and complex constraints.
The core goal of air cargo loading is to reduce the Second, the heuristic search (§ 2.3) ap-
center-of-gravity shift after loading by optimizing, proaches consume a lot of computation time to
thereby saving fuel consumption and increasing calculate solutions under complex constraints. To
aircraft safety. solve the accuracy drop in combinatorial opti-
Since the 1980s, many approaches 3,4 to mization, heuristic search approaches increase the
air cargo loading have been proposed, falling accuracy of the solution by increasing the size of
into the following two categories: combinato- the search space. However, most heuristic search
rial optimization 5,6 and heuristic search. 7–11 How- approaches only consider the cargo features and
ever, since the scenarios of these approaches the loading features in the constraints. Failure
are oversimplified, none of these approaches can to consider cargo hold constraints increases the
achieve high performance under complex con- number of infeasible solutions in the search space,
straints. Oversimplify cargo loading scenarios and it leads to unacceptable searching time costs.
with only three cargo types and four constraints. Therefore, our second challenge is how to effec-
However, in practical loading scenarios, as shown tively reduce the search time and improve the so-
in Figure 1, there exist 13 cargo types and 17 load- lution speed while reducing the loss of search ac-
ing constraints. The limitations of these previous curacy.
approaches are divided into two challenges. In this work, we propose FastLoader, a large
First, the combinatorial optimization (§ 2.2) language model (LLM) 12–18 based optimization
approaches achieve low accuracy under complex method to address the difficulty in optimization
constraints. Most combinatorial optimization ap- problem modeling and the high time consuming
proaches only consider the cargo features and two under complex constraints. The core idea of Fast-
loading features (weight constraint and center-of- Loader is the search space reducer driven by LLM,
gravity constraint) in the constraints. They sac- which effectively reduces the size of the search
rifice the size of the search space to achieve faster space and improves the solution speed. In the
solution speed, but it results in an unsalvage- optimization problem modeling stage, FastLoader
able final solution. This is because under com- models cargo data and complex constraints to
plex constraints, optimization problem modeling form cargo information and LLM engine. In the
is difficult and requires high expertise in scenar- search space reduction stage, FastLoader utilizes
ios. Therefore, simple scenario modeling reduces modeling data to quickly identify infeasible solu-
the accuracy of the solution. The first challenge is tions in the search space and thus simplifies the
739