Page 199 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 199
FastLoader: Leveraging large language models to accelerate cargo loading optimization with numerous
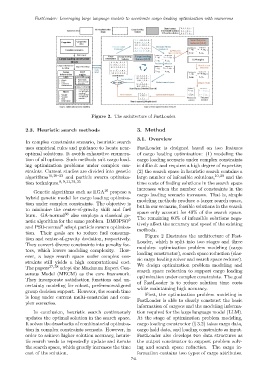
Figure 2. The architecture of FastLoader.
2.3. Heuristic search methods 3. Method
3.1. Overview
In complex constraints scenario, heuristic search
uses empirical rules and guidance to locate near- FastLoader is designed based on two features
optimal solutions. It avoids exhaustive enumera- of cargo loading optimization: (1) modeling the
tion of all options. Such methods suit cargo load- cargo loading scenario under complex constraints
ing optimization problems under complex con- is difficult and requires a high degree of expertise;
straints. Current studies are divided into genetic (2) the search space in heuristic search contains a
algorithms 10,29–33 and particle swarm optimiza- large number of infeasible solutions, 10,29 and the
tion techniques. 8,9,11,34,35 time costs of finding solutions in the search space
increases when the number of constraints in the
Genetic algorithms such as HGA 10 propose a cargo loading scenario increases. That is, simple
hybrid genetic model for cargo loading optimiza-
modeling methods produce a larger search space,
tion under complex constraints. The objective is
but in our scenario, feasible solutions in the search
to minimize the center-of-gravity shift and fuel space only account for 40% of the search space.
burn. GA-normal 36 also employs a classical ge- The remaining 60% of infeasible solutions nega-
netic algorithm for the same problem. DMOPSO 9 tively affect the accuracy and speed of the existing
8
and PSO-normal adopt particle swarm optimiza-
methods.
tion. Their goals are to reduce fuel consump-
Figure 2 illustrates the architecture of Fast-
tion and center-of-gravity deviation, respectively.
Loader, which is split into two stages and three
They convert diverse constraints into penalty fac- modules: optimization problem modeling (cargo
tors, which lowers modeling complexity. How-
ever, a large search space under complex con- loading constructor), search space reduction (clas-
straints still yields a high computational cost. sic cargo loading solver and search space reducer).
The papers 37,38 adopt the Maximum Expert Con- We design optimization problem modeling and
search space reduction to support cargo loading
sensus Model (MECM) as the core framework.
optimization under complex constraints. The goal
They incorporate satisfaction functions and un-
of FastLoader is to reduce solution time costs
certainty modeling for robust, preference-aligned
while maintaining high accuracy.
group decision support. However, the search time
is long under current multi-constraint and com- First, the optimization problem modeling in
plex scenarios. FastLoader is able to clearly construct the basic
information of cargoes and the modeling informa-
In conclusion, heuristic search continuously tion required for the large language model (LLM).
updates the optimal solution in the search space. At the stage of optimization problem modeling,
It solves the drawbacks of combinatorial optimiza- cargo loading constructor (§ 3.2) takes cargo data,
tion in complex constraints scenario. However, in cargo hold data, and loading constraints as input.
order to achieve higher solution accuracy, heuris- FastLoader also develops two data structures as
tic search needs to repeatedly update and iterate the output constructor to support problem solv-
the search space, which greatly increases the time ing and search space reduction. The cargo in-
cost of the solution. formation contains two types of cargo attributes.
741