Page 39 - IJPS-11-4
P. 39
International Journal of
Population Studies Stress in early adulthood
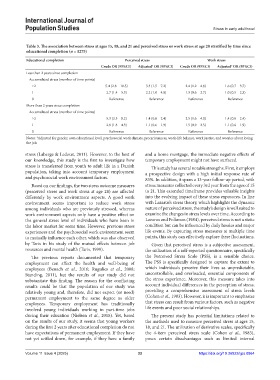
Table 3. The association between stress at ages 15, 18, and 21 and perceived stress or work stress at age 28 stratified by time since
educational completion (n = 1275)
Educational completion Perceived stress Work stress
Crude OR (95%CI) Adjusted OR (95%CI) Crude OR (95%CI) Adjusted OR (95%CI)
†
†
Less than 2 years since completion
Accumulated stress (number of time points)
≥2 5.4 (2.8 – 10.5) 3.3 (1.5 – 7.2) 2.4 (1.2 – 4.8) 1.6 (0.7 – 3.7)
1 2.7 (1.4 – 5.3) 2.2 (1.0 – 4.8) 1.3 (0.6 – 2.7) 1.0 (0.5 – 2.3)
0 Reference Reference Reference Reference
More than 2 years since completion
Accumulated stress (number of time points)
≥2 5.3 (3.5 – 8.2) 1.4 (0.8 – 2.4) 2.5 (1.6 – 4.0) 1.4 (0.8 – 2.4)
1 2.8 (1.8 – 4.3) 1.1 (0.6 – 1.9) 1.5 (0.9 – 2.5) 1.1 (0.6 – 1.9)
0 Reference Reference Reference Reference
Notes: Adjusted for gender, own educational level, psychosocial work climate, precariousness, work-life balance, work justice, and worries about losing
†
the job.
stress (Laberge & Ledoux, 2011). However, to the best of and a home mortgage, the immediate negative effects of
our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate how temporary employment might not have surfaced.
stress is transferred from youth to adult life in a Danish This study has several notable strengths. First, it employs
population, taking into account temporary employment a prospective design with a high initial response rate of
and psychosocial work environment factors. 83%. In addition, it spans a 13-year follow-up period, with
Based on our findings, the two stress outcome measures stress measures collected every 3rd year from the ages of 15
(perceived stress and work stress at age 28) are affected to 21. This extended timeframe provides valuable insights
differently by work environment aspects. A good work into the evolving impact of these stress exposures. In line
environment seems important to reduce work stress with Lazarus’s stress theory, which highlights the dynamic
among individuals who are previously stressed, whereas nature of perceived stress, the study’s design is well suited to
work environment aspects only have a positive effect on examine the changes in stress levels over time. According to
the general stress level of individuals who have been in Lazarus and Folkman (1984), perceived stress is not a static
the labor market for some time. However, previous stress condition but can be influenced by daily hassles and major
experiences and the psychosocial work environment seem life events. By capturing stress measures at multiple time
to mutually influence each other, which was also observed points, this study can effectively explore these fluctuations.
by Taris in his study of the mutual effects between job Given that perceived stress is a subjective assessment,
resources and mental health (Taris, 1999). the utilization of a self-reported questionnaire, specifically
The previous reports documented that temporary the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), is a sensible choice.
employment can affect the health and well-being of The PSS is specifically designed to capture the extent to
employees (Benach et al., 2016; Rugulies et al., 2008; which individuals perceive their lives as unpredictable,
Standing, 2011), but the results of our study did not uncontrollable, and overloaded, essential components of
substantiate this finding. The reason for the conflicting the stress experience. Moreover, this measure takes into
results could be that the population of our study was account individual differences in the perception of stress,
relatively young and, therefore, did not expect (or need) providing a comprehensive assessment of stress levels
permanent employment to the same degree as older (Cohen et al., 1983). However, it is important to emphasize
employees. Temporary employment has traditionally that stress can result from various factors, such as negative
involved young individuals working in part-time jobs life events and poor social relationships.
during their education (Nielsen et al., 2018). Yet, based The present study has potential limitations related to
on the results of our study, it seems that young workers the methods used to measure perceived stress at ages 15,
during the first 2 years after educational completion do not 18, and 21. The utilization of derivative scales, specifically
have expectations of permanent employment. If they have the 4-item perceived stress scale (Cohen et al., 1983),
not yet settled down, for example, if they have a family poses certain disadvantages such as limited internal
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 33 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.0864