Page 22 - IJPS-11-5
P. 22
International Journal of
Population Studies Human behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic
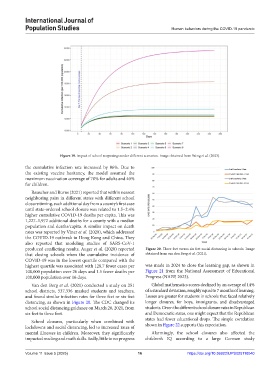
Figure 19. Impact of school reopenings under different scenarios. Image obtained from Weng et al. (2023).
the cumulative infection rate increased by 86%. Due to
the existing vaccine hesitancy, the model assumed the
maximum vaccination coverage of 70% for adults and 40%
for children.
Rauscher and Burns (2021) reported that within nearest
neighboring pairs in different states with different school
closure timing, each additional day from a county’s first case
until state-ordered school closure was related to 1.5–2.4%
higher cumulative COVID-19 deaths per capita. This was
1,227–1,972 additional deaths for a county with a median
population and deaths/capita. A similar impact on death
rates was reported by Viner et al. (2020), which addressed
the COVID-19 outbreak in Hong Kong and China. They
also reported that modeling studies of SARS-CoV-1
produced conflicting results. Auger et al. (2020) reported Figure 20. Three feet versus six feet social distancing in schools. Image
that closing schools when the cumulative incidence of obtained from van den Berg et al. (2021).
COVID-19 was in the lowest quartile compared with the
highest quartile was associated with 128.7 fewer cases per was made in 2024 to close the learning gap, as shown in
100,000 population over 26 days and 1.5 fewer deaths per Figure 21 from the National Assessment of Educational
100,000 population over 16 days. Progress (NAEP, 2023).
Van den Berg et al. (2021) conducted a study on 251 Global mathematics scores declined by an average of 14%
school districts, 537,336 masked students and teachers, of a standard deviation, roughly equal to 7 months of learning.
and found similar infection rates for three feet or six feet Losses are greater for students in schools that faced relatively
distancing, as shown in Figure 20. The CDC changed its longer closures, for boys, immigrants, and disadvantaged
school social distancing guidance on March 20, 2021, from students. Given the different school closure rates in Republican
six feet to three feet. and Democratic states, one might expect that the Republican
states had fewer educational drops. The simple correlation
School closures, particularly when combined with
lockdowns and social distancing, led to increased rates of shown in Figure 22 supports this expectation.
mental illnesses in children. Moreover, they significantly Alarmingly, the school closures also affected the
impacted reading and math skills. Sadly, little to no progress children’s IQ according to a large German study
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 16 https://doi.org/10.36922/IJPS025110040