Page 23 - IJPS-11-5
P. 23
International Journal of
Population Studies Human behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic
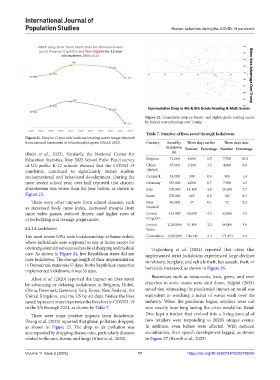
Figure 22. Cumulative drop in fourth- and eighth-grade reading scores
by Biden’s vote advantage over Trump
Table 7. Number of lives saved through lockdowns
Figure 21. Drop in 13 year olds’ math and reading scores. Image obtained
from national assessment of educational progress (NAEP, 2023). Country Saved by Three days earlier Three days later
lockdown Number Percentage Number Percentage
(Breit et al., 2023). Similarly, the National Center for (n)
Education Statistics, May 2022 School Pulse Panel survey Belgium 71,000 4,600 6.5 7,700 10.8
of US public K-12 schools showed that the COVID-19 China 67,000 2,200 3.3 4,000 6.0
pandemic, continued to significantly impair student (Hubei)
socioemotional and behavioral development. During the Denmark 35,000 300 0.9 500 1.4
most recent school year, over half reported that chronic Germany 539,000 4,000 0.7 7,900 1.5
absenteeism was worse than the year before, as shown in Italy 378,000 18,100 4.8 29,100 7.7
Figure 23. Korea 276,000 105 0.0 182 0.1
There were other impacts from school closures, such New 30,000 37 0.1 72 0.2
as increased body mass index, increased myopia from Zealand
more video games, reduced fitness, and higher rates of United 424,000 20,000 4.7 32,000 7.5
cyberbullying and teenage pregnancies. Kingdom
United 2,283,000 51,100 2.2 90,000 3.9
6.2.3.4. Lockdowns States
The most severe NPIs were lockdowns/stay-at-home orders, Cumulative 4,103,000 100,442 2.4 171,454 4.2
where individuals were supposed to stay at home except for
obtaining essential services such as food shopping and medical Trajtenberg et al. (2024) reported that cities that
care. As shown in Figure 24, five Republican states did not implemented strict lockdowns experienced large declines
have lockdowns. The average length of their implementation in robbery, burglary, and vehicle theft, but assault, theft, or
in Democratic states was 57 days. In the Republican states that homicide increased, as shown in Figure 26.
implemented lockdowns, it was 35 days.
Altoè et al. (2020) reported the impact on lives saved Businesses such as restaurants, bars, gyms, and even
by advancing or delaying lockdowns in Belgium, Hubei, churches in some states were shut down. Salpini (2021)
China, Denmark, Germany, Italy, Korea, New Zealand, the noted that witnessing the pandemic’s impact on retail was
United Kingdom, and the US by ±3 days. Notice the lives equivalent to watching a series of waves wash over the
saved represent more than twice the lives lost to COVID-19 industry. When the pandemic began, retailers were not
in the US through 2024, as shown by Table 7. sure exactly how long-lasting the crisis would be. Retail
There were some positive impacts from lockdowns. Dive kept a tracker that evolved into a living journal of
Zheng et al. (2025) reported that global pollution dropped, how retailers were responding to 2020’s unique events.
as shown in Figure 25. The drop in air pollution was In addition, even babies were affected. With reduced
accompanied by dropping disease rates, particularly diseases socialization, their speech development lagged, as shown
related to the ears, throat, and lungs (Altoè et al., 2020). in Figure 27 (Bartelt et al., 2025).
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 17 https://doi.org/10.36922/IJPS025110040