Page 28 - IJPS-11-5
P. 28
International Journal of
Population Studies Human behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic
Not surprisingly, the mental health of those with severe 7.5. Postponed treatments
comorbidities such as Parkinson’s, lupus, inflammatory Widespread delays in medical treatments during the
bowel syndrome, kidney diseases, eating disorders, pandemic have created serious long-term health risks.
or acquired immune deficiency syndrome was more People were hesitant to go to crowded medical facilities.
significantly impacted. Those who exercised, were Furthermore, there were fewer doctors and nurses. Lack
vaccinated, were religious, had positive lifestyles, for of medical insurance also impacted the socioeconomically
example, no smoking, low alcohol, and low body mass disadvantaged. Figure 32 summarizes elective surgery
index, were less impacted. Misinformation increased rates in the US as reported by Butler et al. (2021).
mental health problems, as well.
7.5.1. Cancer
Although there were increased death rates for many
diseases, for example, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and
kidney disease, cancer had some of the largest increases.
Thus, cancer will be used as an illustrative case for the
impact of postponed health care during the pandemic.
Butler et al. (2021) reported that cancer screening rates
were reduced by 70–80% in May 2020. This left a long-
term impact on future cancer rates. They recovered to
prepandemic rates only in February 2023. Angelini et al.
(2022) observed that the risk of death from colon cancer
from delayed treatment increased 6% for every 4 weeks
Figure 30. Years of life lost due to COVID-19 and deaths of despair,
including alcohol-induced causes of death, suicide, and unintentional that surgery was delayed, and that similar delays in
drug overdose in the US in 2020. Image obtained from Entrup et al. (2023). adjuvant chemotherapy for colorectal cancer elevated the
A
B
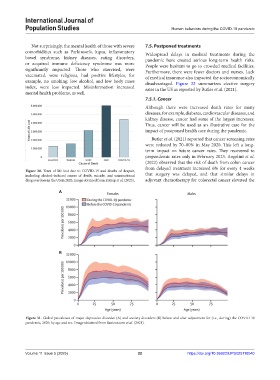
Figure 31. Global prevalence of major depressive disorder (A) and anxiety disorders (B) before and after adjustment for (i.e., during) the COVID-19
pandemic, 2020, by age and sex. Image obtained from Santomauro et al. (2021).
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 22 https://doi.org/10.36922/IJPS025110040