Page 24 - IJPS-11-5
P. 24
International Journal of
Population Studies Human behaviors during the COVID-19 pandemic
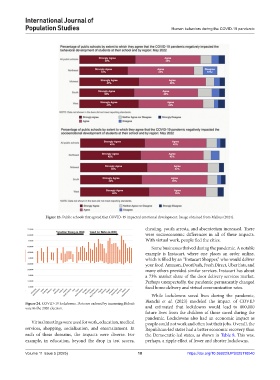
Figure 23. Public schools that agreed that COVID-19 impacted emotional development. Image obtained from Malkus (2024).
cheating, youth arrests, and absenteeism increased. There
were socioeconomic differences in all of these impacts.
With virtual work, people fled the cities.
Some businesses thrived during the pandemic. A notable
example is Instacart, where one places an order online,
which is filled by an “Instacart Shopper,” who would deliver
your food. Amazon, DoorDash, Fresh Direct, Uber Eats, and
many others provided similar services. Instacart has about
a 73% market share of the door delivery services market.
Perhaps unexpectedly, the pandemic permanently changed
food home delivery and virtual communication rates.
While lockdowns saved lives during the pandemic,
Bianchi et al. (2023) modeled the impact of COVID
Figure 24. COVID-19 lockdowns. Data are ordered by increasing Biden’s
vote in the 2020 election. and estimated that lockdowns would lead to 800,000
future lives from the children of those saved during the
pandemic. Lockdowns also had an economic impact as
Virtual meetings were used for work, education, medical people could not work and often lost their jobs. Overall, the
services, shopping, socialization, and entertainment. In Republican-led states had a better economic recovery than
each of these domains, the impacts were diverse. For the Democratic-led states, as shown in Table 8. This was,
example, in education, beyond the drop in test scores, perhaps, a ripple effect of fewer and shorter lockdowns.
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 18 https://doi.org/10.36922/IJPS025110040