Page 117 - IJPS-2-1
P. 117
Mattew O. Oluleke, Akintayo O. Ogunwale, Oyedunni S. Arulogun, et al
Table 4 presents the details of the food avoided by the respondents based on cultural taboos/beliefs.
Pumpkin (45.5%), banana (29.1%), and plantain (19.2%) were avoided because they were believed
to cause depressed fontanelle in babies. Crasscephalum crepidoides (62.5%) and Dioscorea dume-
torum (52.5%) were mentioned as major foods believed to cause belching during delivery. Diets be-
lieved to reduce contraction strength during labor included walnut (59.4%), Dioscorea dumetorum
(6.6%), and Crasscephalum crepidoides (3.8%). Pumpkin (0.6%) was believed to cause slits on
newborns.
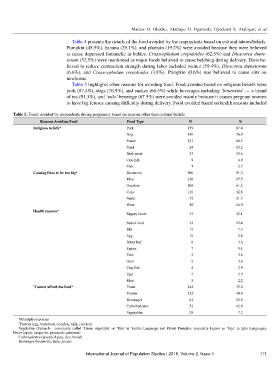
Table 5 highlights other reasons for avoiding food. Food avoided based on religious beliefs were
pork (87.4%), dogs (76.9%), and snakes (66.5%) while beverages including ‘bournvita’ — a brand
of tea (91.3%), and ‘milo’ beverage (67.5%) were avoided mainly because it causes pregnant women
to have big fetuses causing difficulty during delivery. Food avoided based on health reasons included
Table 5. Foods avoided by respondents during pregnancy based on reasons other than cultural beliefs
Reasons Avoiding Food Food Type N %
Religious beliefs* Pork 159 87.4
Dog 140 76.9
Snake 121 66.5
Snail 24 13.2
Bush meat 23 12.6
Crayfish 9 4.9
Fish 5 2.7
Causing fetus to be too big* Bournvita 306 91.3
Milo 226 67.5
Ovaltine 205 61.2
Coke 110 32.8
Fanta 72 21.5
Wine 50’ 14.9
Health reasons* Sugary foods 44 32.1
Salted food 32 23.4
Eba 15 7.3
Egg 10 5.8
Bitter leaf 8 3.6
Spices 7 5.1
Yam 5 3.6
Okro 5 3.6
Crayfish 4 2.9
Ugu 4 2.9
Meat 3 2.2
+ Cannot afford the food* Fruits 142 35.0
Protein 122 30.0
Beverages 61 15.0
Carbohydrates 52 12.8
Vegetables 29 7.2
*Multiple responses
+ Protein (egg, bushmeat, crayfish, milk, chicken)
Vegetables (Spinach- commonly called ‘Green vegetable’ or ‘Tete’ in Yoruba Language and Fluted Pumpkin- popularly known as ‘Ugu’ in Igbo Language),
Fruits (apple, tangerine, pineapple, pawpaw)
Carbohydrates (pounded yam, rice, bread)
Beverages (bournvita, milo, juices)
International Journal of Population Studies | 2016, Volume 2, Issue 1 111