Page 63 - IJPS-7-1
P. 63
Ntoimo
Table 1. (Continued)
Characteristic Frequency Percent (%)
(N=13,674)
Number of respondent’s sibling
0 – 2 1,714 12.54
3 – 4 3,537 25.87
5 – 6 4,145 30.31
7+ 4,278 31.28
Number of co-wives
Monogamous 10,838 79.26
Polygynous 2,836 20.74
Experience of child death
No 11,480 83.96
Yes 2,194 16.04
Age at first marriage
<20 7,693 56.26
20+ 5,981 43.74
Year of marriage
2008 – 2013 7,902 57.79
2014 – 2018 5,772 42.21
The frequency may not equal the N due to
rounding
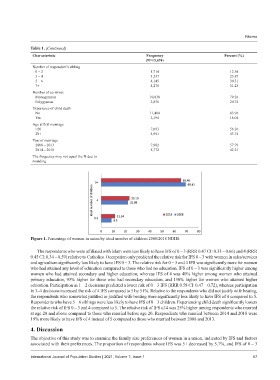
Figure 1. Percentage of women in union by ideal number of children 2008/2018 NDHS.
The respondents who were affiliated with Islam were less likely to have IFS of 0 – 3 (RRR 0.47 CI: 0.33 – 0.66) and 4 (RRR
0.45 CI: 0.34 – 0.59) relative to Catholics. Occupation only predicted the relative risk for IFS 0 – 3 with women in sales/services
and agriculture significantly less likely to have IFS 0 – 3. The relative risk for 0 – 3 and 4 IFS was significantly more for women
who had attained any level of education compared to those who had no education. IFS of 0 – 3 was significantly higher among
women who had attained secondary and higher education; whereas IFS of 4 was 40% higher among women who attained
primary education, 93% higher for those who had secondary education, and 130% higher for women who attained higher
education. Participation in 1 – 2 decisions predicted a lower risk of 0 – 3 IFS (RRR 0.58 CI: 0.47 – 0.72), whereas participation
in 3–4 decisions increased the risk of 4 IFS compared to 5 by 51%. Relative to the respondents who did not justify wife beating,
the respondents who somewhat justified or justified wife beating were significantly less likely to have IFS of 4 compared to 5.
Respondents who have 5 – 6 siblings were less likely to have IFS of 0 – 3 children. Experiencing child death significantly lowers
the relative risk of IFS 0 – 3 and 4 compared to 5. The relative risk of IFS of 4 was 25% higher among respondents who married
at age 20 and above compared to those who married before age 20. Respondents who married between 2014 and 2018 were
19% more likely to have IFS of 4 instead of 5 compared to those who married between 2008 and 2013.
4. Discussion
The objective of this study was to examine the family size preferences of women in a union, indicated by IFS and factors
associated with their preferences. The proportion of respondents whose IFS was 5+ decreased by 5.7%, and IFS of 0 – 3
International Journal of Population Studies | 2021, Volume 7, Issue 1 57