Page 61 - IJPS-9-2
P. 61
International Journal of
Population Studies Personality traits in homosexual men in Iran
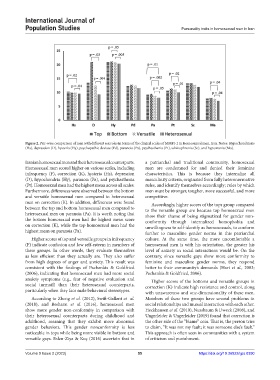
Figure 2. Pair-wise comparison of men with different sex roles in terms of the clinical scales of MMPI-2 in Homosexual men, Iran. Notes: Hypochondriasis
(Hs), depression (D), hysteria (Hy), psychopathic deviate (Pd), paranoia (Pa), psychasthenia (Pt), schizophrenia (Sc), and hypomania (Ma).
Iranian homosexual men and their heterosexual counterparts. a patriarchal and traditional community, homosexual
Homosexual men scored higher on various scales, including men are condemned for and denied their feminine
infrequency (F), correction (K), hysteria (Hs), depression characteristics. This is because they internalize all
(D), hypochondria (Hy), paranoia (Pa), and psychasthenia masculinity criteria, originated from fully heteronormative
(Pt). Homosexual men had the highest mean across all scales. rules, and identify themselves accordingly; rules by which
Furthermore, differences were observed between the bottom men must be stronger, tougher, more successful, and more
and versatile homosexual men compared to heterosexual competitive.
men on correction (K). In addition, differences were found Accordingly, higher scores of the tops group compared
between the top and bottom homosexual men compared to to the versatile group are because top homosexual men
heterosexual men on paranoia (Pa). It is worth noting that show their shame of being stigmatized for gender non-
the bottom homosexual men had the highest mean score conformity through internalized homophobia and
on correction (K), while the top homosexual men had the unwillingness to self-identify as homosexuals, to conform
highest mean on paranoia (Pa). further to masculine gender norms in this patriarchal
Higher scores of top and versatile groups in infrequency culture. At the same time, the more uncomfortable a
(F) indicate confusion and low self-esteem in members of homosexual men is with his orientation, the greater his
these groups. In other words, they evaluate themselves level of anxiety in social interactions would be. On the
as less efficient than they actually are. They also suffer contrary, since versatile gays show more conformity to
from high degrees of anger and anxiety. This result was feminine and masculine gender norms, they respond
consistent with the findings of Pachankis & Goldfried better to their community’s demands (Hart et al., 2003;
(2006), indicating that homosexual men had more social Pachankis & Goldfried, 2006).
anxiety symptoms (e.g., fear of negative evaluation and Higher scores of the bottoms and versatile groups in
social turmoil) than their heterosexual counterparts, correction (K) indicate high resistance and control, along
particularly when they face male behavioral stereotypes. with unawareness and one-dimensionality of these men.
According to Zheng et al. (2012), Swift-Gallant et al. Members of these two groups have several problems in
(2018), and Besharat et al. (2016), homosexual men social relationships and mutual interaction with each other.
show more gender non-conformity in comparison with Heckhausen et al. (2010), Nussbaum & Dweck (2008), and
their heterosexual counterparts during childhood and Ungerleider & Ungerleider (2019) found that correction is
adulthood, meaning that they exhibit more abnormal the other side of the “blame” coin. That is, the person tries
gender behaviors. This gender nonconformity is less to claim, “It was not my fault; it was someone else’s fault.”
noticeable in tops while being more visible in bottom and This approach is often seen in communities with a system
versatile gays. Eslen-Ziya & Koç (2016) ascertain that in of criticism and punishment.
Volume 9 Issue 2 (2023) 55 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.0390