Page 39 - IMO-2-3
P. 39
Innovative Medicines & Omics Tyrosine kinases: Structure, mechanism, and therapeutics
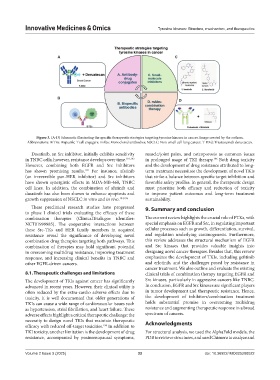
A C
B
D
Figure 3. (A-D) Schematic illustrating the specific therapeutic strategies targeting tyrosine kinases in cancer. Image created by the authors.
Abbreviations: BiTEs: Bispecific T cell engagers; mAbs: Monoclonal antibodies; NSCLC: Non-small cell lung cancer; T-DXd: Trastuzumab deruxtecan.
Dasatinib, an Src inhibitor, initially exhibits sensitivity muscle/joint pains, and osteoporosis as common issues
in TNBC cells; however, resistance develops over time. 191,192 in prolonged usage of TKI therapy. Both drug toxicity
196
However, combining both EGFR and Src inhibitors and the development of drug resistance attributed to long-
193
has shown promising results. For instance, afatinib term treatment necessitate the development of novel TKIs
(an irreversible pan-HER inhibitor) and Src inhibitors that strike a balance between specific target inhibition and
have shown synergistic effects in MDA-MB-468, TNBC favorable safety profiles. In general, the therapeutic design
cell lines. In addition, the combination of afatinib and must prioritize both efficacy and reduction of toxicity
dasatinib has also been shown to enhance apoptosis and to improve patient outcomes and long-term treatment
growth suppression of NSCLC in vitro and in vivo. 194,195 sustainability.
These preclinical research studies have progressed 9. Summary and conclusion
to phase I clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of these
combination therapies (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: The current review highlights the crucial role of PTKs, with
NCT01999985). The cooperative interactions between special emphasis on EGFR and Src, in regulating important
these Src-TKs and HER family members in acquired cellular processes such as growth, differentiation, survival,
resistance reveal the significance of developing novel and regulation underlying carcinogenesis. Furthermore,
combination drug therapies targeting both pathways. This this review addresses the structural mechanism of EGFR
combination of therapies may hold significant potential and Src kinases that provides valuable insights into
in overcoming multidrug resistance, improving treatment designing novel cancer therapies. Besides that, this review
response, and increasing clinical benefits in TNBC and emphasizes the development of TKIs, including gefitinib
other EGFR-driven cancers. and erlotinib, and the challenges posed by resistance in
cancer treatment. We also outline and evaluate the existing
8.1. Therapeutic challenges and limitations clinical trials of combination therapy targeting EGFR and
The development of TKIs against cancer has significantly Src kinases, particularly in aggressive cancers like TNBC.
advanced in recent years. However, their clinical utility is In conclusion, EGFR and Src kinases are significant players
often reduced by the extra-cardio adverse effects due to in tumor development and therapeutic resistance. Hence,
toxicity. It is well documented that older generations of the development of inhibitors/combination treatment
TKIs can cause a wide range of cardiovascular issues such holds substantial promise in overcoming multidrug
as hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and heart failure. These resistance and augmenting therapeutic response in a broad
adverse effects highlight a critical therapeutic challenge: the spectrum of cancers.
necessity to design novel TKIs that maintain therapeutic Acknowledgments
196
efficacy with reduced off-target toxicities. In addition to
TKI toxicity, another limitation is the development of drug For structural analysis, we used the AlphaFold models, the
resistance, accompanied by postmenopausal symptoms, PDB to retrieve structures, and used Chimera to analyze and
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/IMO025200022