Page 36 - IMO-2-3
P. 36
Innovative Medicines & Omics Tyrosine kinases: Structure, mechanism, and therapeutics
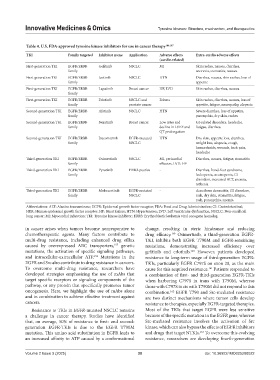
Table 4. U.S. FDA-approved tyrosine kinase inhibitors for use in cancer therapy 146,147
TKI Family targeted Inhibitor name Application Adverse effects Extra-cardio adverse effects
(cardio-related)
First-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Gefitinib NSCLC MI Skin rashes, nausea, diarrhea,
family anorexia, stomatitis, nausea
First-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Icotinib NSCLC HTN Diarrhea, nausea, skin rashes, loss of
family appetite
First-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Lapatinib Breast cancer HF, LVD Skin rashes, diarrhea, nausea
family
First-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Erlotinib NSCLC and Edema Skin rashes, diarrhea, nausea, loss of
family prostate cancer appetite, fatigue, neuropathy, alopecia
Second-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Afatinib NSCLC HTN Severe diarrhea, loss of appetite,
family paronychia, dry skin, rashes
Second-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Neratinib Breast cancer Low rates and GI-related disorders, headache,
family decline in LVEF and fatigue, diarrhea
QT prolongation
Second-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Dacomitinib EGFR-mutated HTN Dry skin, appetite loss, diarrhea,
family NSCLC weight loss, alopecia, cough,
hemorrhoids, wounds, back pain,
headache
Third-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Osimertinib NSCLC MI, pericardial Diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, stomatitis
family effusion, LVD, HF
Third-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Pyrotinib HER2-postive - Diarrhea, hand-foot syndrome,
family leukopenia, neutropenia, GI
disorders, increased ALT, anemia,
asthenia
Third-generation TKI EGFR/ERBB Mobocertinib EGFR-mutated - Acneiform dermatitis, GI disorders,
family NSCLC rash, dry skin, stomatitis, fatigue,
rash, paronychia, anemia
Abbreviations: ALT: Alanine transaminase; EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; FDA: Food and Drug Administration; GI: Gastrointestinal;
HER: Human epidermal growth factor receptor; HF: Heart failure; HTN: Hypertension; LVD: Left ventricular dysfunction; NSCLC: Non-small cell
lung cancer; MI: Myocardial infarction; TKI: Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; ERBB: Erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene homolog.
in cancer arises when tumors become nonresponsive to change, resulting in steric hindrance and reducing
chemotherapeutic agents. Many factors contribute to drug efficacy. Osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR-
159
multi-drug resistance, including enhanced drug efflux TKI, inhibits both EGFR T790M and EGFR-sensitizing
caused by overexpressed ABC transporters, genetic mutations, demonstrating increased efficiency over
157
mutations, the activation of specific signaling pathways, gefitinib and erlotinib. However, patients developed
160
and intracellular-extracellular ATP. Mutations in the resistance to long-term usage of third-generation EGFR-
158
EGFR and Src also contribute to drug resistance in cancers. TKIs, particularly EGFR C797S on exon 20, as the main
To overcome multi-drug resistance, researchers have cause for this acquired resistance. Patients responded to
161
developed strategies emphasizing the use of mAbs that a combination of first- and third-generation EGFR-TKIs
target specific receptors or signaling components of the when harboring C797S in trans with T790M, whereas
pathway, or any protein that specifically promotes tumor those with C797S in cis with T790M did not respond to this
oncogenesis. Here, we highlight the use of mAbs alone combination. EGFR T790 and Src-mediated resistance
162
and in combination to achieve effective treatment against are two distinct mechanisms where tumor cells develop
cancers. resistance to therapies, especially EGFR-targeted therapies.
Resistance to TKIs in EGFR-mutated NSCLC remains Most of the TKIs that target EGFR were less sensitive
a challenge in cancer therapy. Studies have identified because of the specific mutation in the EGFR gene, whereas
that, on average, 50% of resistance to first- and second- Src-mediated resistance involves the activation of Src
generation EGFR-TKIs is due to the EGFR T790M kinase, which can also bypass the effects of EGFR inhibitors
163
mutation. This amino acid substitution in EGFR leads to and drugs that target NTKIs. To overcome this evolving
an increased affinity to ATP caused by a conformational resistance, researchers are developing fourth-generation
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 30 doi: 10.36922/IMO025200022