Page 44 - ITPS-5-2
P. 44
38 INNOSC Theranostics and Pharmacological Sciences, 2022, Vol. 5, No. 2 Das et al.
A B
C
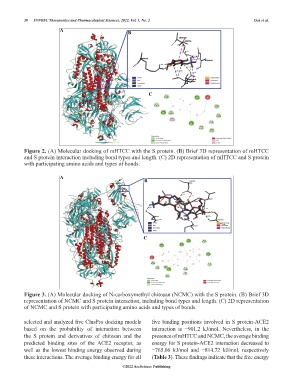
Figure 2. (A) Molecular docking of mHTCC with the S protein. (B) Brief 3D representation of mHTCC
and S protein interaction including bond types and length. (C) 2D representation of mHTCC and S protein
with participating amino acids and types of bonds.
A
B
C
Figure 3. (A) Molecular docking of N-carboxymethyl chitosan (NCMC) with the S protein. (B) Brief 3D
representation of NCMC and S protein interaction, including bond types and length. (C) 2D representation
of NCMC and S protein with participating amino acids and types of bonds.
selected and analyzed five ClusPro docking models five binding positions involved in S protein-ACE2
based on the probability of interaction between interaction is −901.2 kJ/mol. Nevertheless, in the
the S protein and derivatives of chitosan and the presence of mHTCC and NCMC, the average binding
predicted binding sites of the ACE2 receptor, as energy for S protein-ACE2 interaction decreased to
well as the lowest binding energy observed during −765.06 kJ/mol and −814.72 kJ/mol, respectively
these interactions. The average binding energy for all (Table 3). These findings indicate that the free energy
©2022 AccScience Publishing