Page 46 - ITPS-6-1
P. 46
40 INNOSC Theranostics and Pharmacological Sciences, 2023, Vol. 6, No. 1 Hariharan
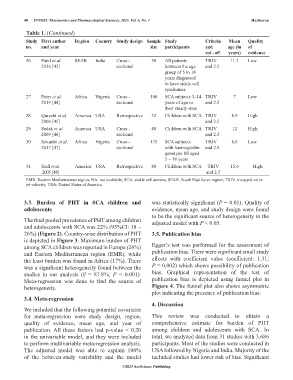
Table 1. (Continued)
Study First author Region Country Study design Sample Study Criteria Mean Quality
no. and year size participants and age (in of
cut ‑ off years) evidence
26 Patel et al. SEAR India Cross - 50 All patients TRJV 11.3 Low
2016 [43] sectional between the age and 2.5
group of 5 to 18
years diagnosed
to have sickle cell
syndromes
27 Peter et al. Africa Nigeria Cross - 100 SCA subjects 3–14 TRJV 7 Low
2019 [44] sectional years of age in and 2.5
their steady state
28 Qureshi et al. America USA Retrospective 32 Children with SCA TRJV 8.9 High
2006 [45] and 2.5
29 Sedak et al. America USA Cross - 48 Children with SCA TRJV 12 High
2009 [46] sectional and 2.5
30 Sokunbi et al. Africa Nigeria Cross - 175 SCA subjects TRJV 8.8 Low
2017 [47] sectional with haemoglobin and 2.5
genotype SS aged
5 – 18 years
31 Suell et al. America USA Retrospective 80 Children with SCA TRJV 15.6 High
2005 [48] and 2.5
EMR: Eastern Mediterranean region; NA: not available; SCA: sickle cell anemia; SEAR: South East Asian region; TRJV: tricuspid valve
jet velocity; USA: United States of America
3.3. Burden of PHT in SCA children and was statistically significant (P = 0.01). Quality of
adolescents evidence, mean age, and study design were found
to be the significant source of heterogeneity in the
The final pooled prevalence of PHT among children adjusted model with P < 0.05.
and adolescents with SCA was 22% (95%CI: 18 –
26%) (Figure 2). Country-wise distribution of PHT 3.5. Publication bias
is depicted in Figure 3. Maximum burden of PHT
among SCA children was reported in Europe (26%) Egger’s test was performed for the assessment of
and Eastern Mediterranean region (EMR), while publication bias. There were significant small study
the least burden was found in Africa (17%). There effects with coefficient value (coefficient: 1.31;
was a significant heterogeneity found between the P = 0.002) which shows possibility of publication
studies in our analysis (I = 87.8%; P < 0.001). bias. Graphical representation of the test of
2
Meta-regression was done to find the source of publication bias is depicted using funnel plot in
heterogeneity. Figure 4. The funnel plot also shows asymmetric
plot indicating the presence of publication bias.
3.4. Meta-regression
4. Discussion
We included that the following potential covariates
for meta-regression were study design, region, This review was conducted to obtain a
quality of evidence, mean age, and year of comprehensive estimate for burden of PHT
publication. All these factors had p-value < 0.20 among children and adolescents with SCA. In
in the univariable model, and they were included total, we analyzed data from 31 studies with 3,686
to perform multivariable meta-regression analysis. participants. Most of the studies were conducted in
The adjusted model was able to explain 100% USA followed by Nigeria and India. Majority of the
of the between-study variability and the model included studies had lower risk of bias. Significant
©2023 AccScience Publishing