Page 62 - ITPS-6-2
P. 62
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Tryptophan and schizophrenia
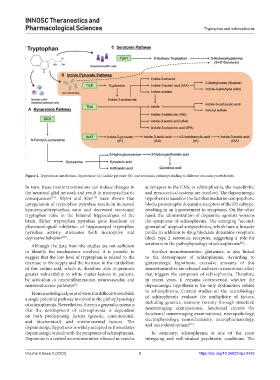
Figure 2. Tryptophan metabolism. Kynurenine (A), indole pyruvate (B), and serotonin pathways leading to different secondary metabolites.
In turn, these neurotransmissions can induce changes in at synapses in the CNS; in schizophrenia, the mesolimbic
the neuronal-glial network and result in neuropsychiatric and mesocortical systems are involved. The dopaminergic
consequences . Myint and Kim have shown that hypothesis is based on the fact that mediation antipsychotic
[19]
[19]
upregulation of tryptophan pyrrolase results in increased blocks postsynaptic dopamine receptors of the D2 subtype,
kynurenine/tryptophan ratio and decreased serotonin/ resulting in an improvement in symptoms. On the other
tryptophan ratio in the bilateral hippocampus of the hand, the administration of dopamine agonists worsens
brain. Either tryptophan pyrrolase gene knockout or the symptoms of schizophrenia. The emerging “second-
pharmacological inhibition of hippocampal tryptophan generation” atypical antipsychotics, which have a broader
pyrrolase activity attenuates both nociceptive and profile in addition to drug blockade dopamine receptors,
depressive behavior . block type 2 serotonin receptors, suggesting a role for
[20]
[21]
Although the data from the studies are not sufficient serotonin in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia .
to identify the mechanisms involved, it is possible to Another neurotransmitter, glutamate, is also linked
suggest that the low level of tryptophan is related to the to the development of schizophrenia. According to
decrease in the supply and the increase in the catabolism glutamatergic hypothesis, excessive amounts of this
of this amino acid, which is, therefore, able to promote neurotransmitter are released and exert a neurotoxic effect
greater vulnerability to white matter lesions in patients, that triggers the symptoms of schizophrenia. Therefore,
by activation of neuroinflammation, neurovascular, and in recent years, it remains controversial whether the
neuroendocrine pathways . dopaminergic hypothesis is the only dysfunction related
[2]
From an etiological point of view, it is difficult to establish to schizophrenia. Current studies on the neurobiology
a single potential pathway involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia evaluate the multiplicity of factors,
of schizophrenia. Nevertheless, there is a general consensus including genetics, anatomy (mainly through structural
that the development of schizophrenia is dependent neuroimaging examinations), functional circuits (by
on both predisposing factors (genetic, constitutional, functional neuroimaging examinations), neuropathology,
and biochemical) and environmental factors. The electrophysiology, neurochemistry, neuropharmacology,
[22]
dopaminergic hypothesis is widely accepted as it associates and neurodevelopment .
dopaminergic stimuli with the symptoms of schizophrenia. In summary, schizophrenia is one of the most
Dopamine is a central neurotransmitter released in vesicles intriguing and well-studied psychiatric conditions. The
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2023) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.0435