Page 61 - ITPS-6-2
P. 61
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Tryptophan and schizophrenia
When there is a deficiency of niacin (vitamin B3)
in the body, tryptophan can be used for the synthesis of
the essential cofactor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
(NAD ), which is an important carrier of electrons and
+
fundamental in the production of energy for the cell .
[12]
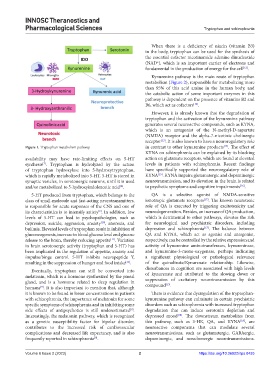
Kynurenine pathway is the main route of tryptophan
metabolism (Figure 2), responsible for metabolizing more
than 95% of this acid amine in the human body, and
the catabolic action of some important enzymes in this
pathway is dependent on the presence of vitamins B2 and
B6, which act as cofactors .
[10]
However, it is already known that the degradation of
tryptophan and the activation of the kynurenine pathway
generates several neuroactive compounds, such as KYNA,
which is an antagonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate
(NMDA) receptor and the alpha-7-nicotinic cholinergic
[13]
receptor . It is also known to have a neuroregulatory role
[14]
Figure 1. Tryptophan metabolism pathway. in contrast to other kynurenine products . The effect of
KYNA on schizophrenia can be explained by its blocking
availability may have rate-limiting effects on 5-HT action on glutamate receptors, which are found at elevated
synthesis . Tryptophan is hydrolyzed by the action levels in patients with schizophrenia. Recent findings
[7]
of tryptophan hydroxylase into 5-hydroxytryptophan, have specifically supported the neuroregulatory role of
which is rapidly metabolized into 5-HT. 5-HT is stored in KYNA . KYNA impairs glutamatergic and dopaminergic
[15]
synaptic vesicles, in serotonergic neurons, until it is used neurotransmission, and its elevation in the brain is related
[16]
and/or metabolized to 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid . to psychotic symptoms and cognitive impairments .
[8]
5-HT produced from tryptophan, which belongs to the QA is a selective agonist of NMDA-sensitive
class of small-molecule and fast-acting neurotransmitters, ionotropic glutamate receptors . The known neurotoxic
[17]
is responsible for acute responses of the CNS and one of role of QA is executed by triggering excitotoxicity and
its characteristics is to intensify satiety . In addition, low neurodegeneration. Besides, an increase of QA production,
[9]
levels of 5-HT can lead to psychopathologies, such as which is detrimental to other pathways, elevates the risk
depression, suicide, aggression, anxiety , anorexia, and for neurological and psychiatric disorders, including
[10]
bulimia. Elevated levels of tryptophan result in inhibition of depression and schizophrenia . The balance between
[17]
gluconeogenesis, increase in blood glucose level and glucose QA and KYNA, which act as agonist and antagonist,
release to the brain, thereby reducing appetite . Variation respectively, can be controlled by the relative expression and
[11]
in brain serotonergic activity (tryptophan and 5-HT) has activity of kynurenine aminotransferases, kynureninase,
been implicated in the regulation of appetite, anxiety and and kynurenine-3-mono-oxygenase, perhaps indicating
impulse/binge control. 5-HT inhibits neuropeptide Y, a significant physiological or pathological relevance
resulting in the suppression of hunger and food intake . of the quinolinate/Kynurenate relationship. Likewise,
[11]
disturbances in cognition are associated with high levels
Eventually, tryptophan can still be converted into
melatonin, which is a hormone synthesized by the pineal of kynurenate and attributed to the slowing down or
suppression of excitatory neurotransmission by this
gland, and is a hormone related to sleep regulation in compound .
[13]
humans . It is also important to mention that, although
[9]
it is known to be found in lower concentrations in patients There is evidence that dysregulation of the tryptophan-
with schizophrenia, the importance of melatonin for some kynurenine pathway can culminate in certain psychiatric
specific symptoms of schizophrenia and in inhibiting some disorders such as schizophrenia with increased tryptophan
side effects of antipsychotics is still underestimated . degradation that can induce serotonin depletion and
[9]
Interestingly, the melatonin pathway, which is recognized depressed mood . The downstream metabolites from
[18]
as a genetic susceptibility factor for bipolar disorder, this pathway, such as 3-HK, QA, and KYNA , are
[18]
contributes to the increased risk of cardiovascular neuroactive components that can modulate several
complications and decreased life expectancy, and is also neurotransmissions, such as glutamatergic, GABAergic,
frequently reported in schizophrenia . dopaminergic, and noradrenergic neurotransmissions.
[9]
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.0435