Page 128 - ITPS-7-2
P. 128
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences PI3K-α inhibitors for cancer immunotherapy
amino acid residues around a ligand is crucial to driving
coherent functional control of biomolecules. Hence, from
93
our simulation result, the formation of a hydrophobic core
by the numerous hydrophobic amino acid residues around
T85 demonstrated a strong interaction that indicated
adequate ligand-receptor stability, binding specificity, and
selectivity.
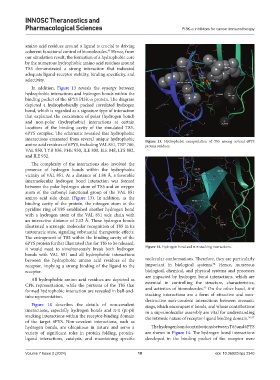
In addition, Figure 13 reveals the synergy between
hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds within the
binding pocket of the 6PYS PI3K-α protein. The diagram
depicted a hydrophobically packed correlated hydrogen
bond, which is regarded as a signature type of interaction
that explained the coexistence of polar (hydrogen bond)
and non-polar (hydrophobic) interactions at certain
locations of the binding cavity of the simulated T85-
6PYS complex. The schematic revealed that hydrophobic
interactions emanated from several unique hydrophobic Figure 13. Hydrophobic encapsulation of T85 among several 6PYS
amino acid residues of 6PYS, including VAL 851, TRP 780, protein residues.
VAL 850, TYR 836, PHE 930, ILE 800, ILE 848, LYS 802,
and ILE 932.
The complexity of the interactions also involved the
presence of hydrogen bonds within the hydrophobic
vicinity of VAL 851. At a distance of 1.88 Å, a favorable
intermolecular hydrogen bond interaction was formed
between the polar hydrogen atom of T85 and an oxygen
atom of the carbonyl functional group of the VAL 851
amino acid side chain (Figure 13). In addition, in the
binding cavity of the protein, the nitrogen atom in the
pyridine ring of T85 established another hydrogen bond
with a hydrogen atom of the VAL 851 side chain with
an interactive distance of 2.12 Å. These hydrogen bonds
illustrated a strategic molecular recognition of T85 in its
tautomeric state, signaling substantial therapeutic effects.
The entrapment of T85 within the binding cavity of the
6PYS protein further illustrated that for T85 to be released,
it would need to simultaneously break both hydrogen Figure 14. Hydrogen bond and π-π stacking interactions.
bonds with VAL 851 and all hydrophobic interactions
between the hydrophobic amino acid residues of the molecular conformations. Therefore, they are particularly
94
receptor, implying a strong binding of the ligand to the important in biological systems. Hence, numerous
receptor. biological, chemical, and physical systems and processes
are impacted by hydrogen bond interactions, which are
All hydrophobic amino acid residues are depicted as
CPK representation, while the portions of the T85 that essential in controlling the structure, characteristics,
95
formed hydrophobic interaction are revealed in ball-and- and activities of biomolecules. On the other hand, π-π
tube representation. stacking interactions are a form of attractive and non-
destructive non-covalent interactions between aromatic
Figure 14 describes the details of non-covalent rings, which encompass π bonds, and whose contributions
interactions, especially hydrogen bonds and π-π (pi-pi) in a supramolecular assembly are vital for understanding
stacking interactions within the receptor-binding domain the intrinsic nature of receptor-ligand binding domain. 96,97
of the target 6PYS. Non-covalent interactions, such as
hydrogen bonds, are ubiquitous in nature and serve a The hydrogen bond contributions between T85 and 6PYS
variety of significant roles in protein folding, protein- are shown in Figure 14. The hydrogen bond interactions
ligand interactions, catalysis, and maintaining specific developed in the binding pocket of the receptor were
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2024) 18 doi: 10.36922/itps.2340