Page 12 - ITPS-7-3
P. 12
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Therapeutic value of terpenes
Table 2. Examples of monoterpenoids and sesquiterpenoids of C. sativa primarily stem from its secondary metabolites,
profiled in cannabis inflorescences, leaves, stem bars, and such as cannabinoids and terpenoids, the profiles of which
roots for medicinal purposes vary across cannabis strains. Hence, it is suggested that
these secondary metabolites work synergistically in a
Terpenoids Examples phenomenon known as the entourage effect to produce
Mono-terpenoids α-Pinene; eucalyptol; borneol; camphene; ocimene; an enhanced pharmacological effect in humans. 61,62
terpinen-4-ol; sabinene; γ-terpinene; terpineol;
(-)-β-pinene; sabinene hydrate; (+)-dihydrocarvone; This phytocannabinoid-terpenoid synergy could also
β-myrcene; terpinolene; nerol; α-phellandrene; be beneficial in the treatments of microbial infections,
frenchone; pulegone; Δ -carene; linalool; carvone; mental disorders, pain, inflammation, nociception, insulin
3
α-terpinene; frenchol; geraniol; p-cymene; resistance, diabetes, and comorbidities. 61,63-66 In this review,
(-)-isopulegol; geranyl acetate; limonene; camphor. we will focus on the medicinal value of terpenoids instead
Sesqui-terpenoids (-)-β-Elemene; viridiflorol; β-caryophyllene; of cannabinoids and their synergistic effects. Nonetheless,
(-)-guaiol; aromadendrene; (+)-cedrol;
trans-β-farnesene; β-eudesmol; α-humulene; the terpenes of the cannabis plant have been well studied,
α-bisabolol; valencene; ledene; trans-nerolidol; and they shall be used as a reference in this review when
caryophyllene oxide; globulol. discussing terpenes.
Over 150 different terpenes and 100 cannabinoids
(e.g., tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol, and cannabigerol)
are produced in a resin that forms within glandular trichomes
located on the surfaces of pistillate inflorescences as well as
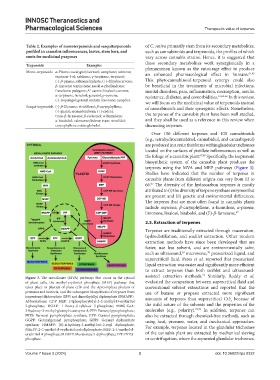
the foliage of a cannabis plant. 67,68 Specifically, the isoprenoid
biosynthetic system of the cannabis plant produces the
terpenes using the MVA and MEP pathways (Figure 3).
Studies have indicated that the number of terpenes in
cannabis plants from different origins can vary from 12 to
66. The diversity of the hydrocarbon terpenes is mostly
67
attributed to (i) the diversity of terpene synthase enzymes that
are present and (ii) genetic and environmental differences.
The terpenes that are most often found in cannabis plants
include myrcene, β-caryophyllene, α-humulene, α-pinene,
limonene, linalool, bisabolol, and (E)-β-farnesene. 67
2.3. Extraction of terpenes
Terpenes are traditionally extracted through maceration,
hydrodistillation, and soxhlet extraction. Other modern
extraction methods have since been developed that are
faster, use less solvent, and are environmentally safer,
such as ultrasound, microwave, pressurized liquid, and
69
70
supercritical fluid. Peres et al. reported that pressurized
liquid extraction was easier and significantly more efficient
to extract terpenes than both soxhlet and ultrasound-
71
Figure 3. The mevalonate (MVA) pathways that occur in the cytosol assisted extraction methods. Similarly, Reddy et al.
of plant cells, the methyl-erythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway that evaluated the comparison between supercritical fluid and
takes place in plastids of plant cells and the Apicomplexa phylum of conventional solvent extractions and reported that the
protozoa and bacteria, and the subsequent biosynthesis of terpenes from use of butane or propane extracted more significant
isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) amounts of terpenes than supercritical CO because of
Abbreviations: CDP MEP: Diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2
2-phosphate; DOXP: 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate; HMG-CoA: the mild nature of the solvents and the properties of the
3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A; FPP: Farnesyl pyrophosphate; molecules (e.g., polarity). 72,73 In addition, terpenes can
FPPS: Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase; GPP: Geranyl pyrophosphate; also be extracted through chemical-free methods, such as
GGPP: Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate; GPPS: Geranyl diphosphate using heat, pressure, water, and mechanical approaches.
synthase; HMBPP: (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl diphosphate; For example, terpenes located in the glandular trichomes
MEcPP: 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol cyclodiphosphate; MEP: 2-C-methyl-d-
erythritol-4-phosphate; MVAPP: Mevalonate 5-diphosphate; PPP: PPP:3- of the cannabis plant are extracted by mechanical sieving
phosphate. or centrifugation, where the separated glandular trichomes,
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 3 doi: 10.36922/itps.0332