Page 16 - ITPS-7-3
P. 16
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Therapeutic value of terpenes
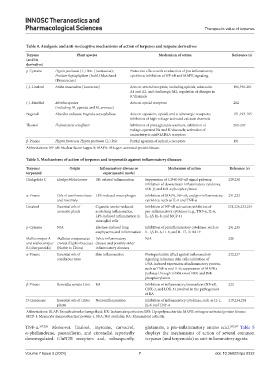
Table 4. Analgesic and anti‑nociceptive mechanisms of action of terpenes and terpene derivatives
Terpene Plant species Mechanism of action Reference (s)
(and its
derivative)
p-Cymene Hyptis pectinata (L.) Poit. (Lamiaceae); Protective effects with a reduction of pro-inflammatory
Protium heptaphyllum (Aubl.) Marchand cytokines; inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling
(Burseraceae)
(-)-Linalool Aniba rosaeodora (Lauraceae) Acts on several receptors, including opioids, adenosine 196,198-201
A1 and A2, and cholinergic M2; regulation of changes in
K channels
+
(-)-Menthol Mentha species Acts on opioid receptors 202
(including M. piperita and M. arvensis)
Eugenol Abutilon indicum; Eugenia caryophyllata Acts on capsaicin, opioid, and α-adrenergic receptors; 151,193-195
inhibition of high-voltage-activated calcium channels
Thymol Hofmeisteria schaffneri Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis; inhibition of 203-207
voltage-operated Na and K channels; activation of
+
+
aminobutyric acid GABAA receptors
β-Pinene Hyptis fruticosa; Hyptis pectinata (L.) Poit Partial agonism of opioid μ receptors 191
Abbreviations: NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase.
Table 5. Mechanisms of action of terpenes and terpenoids against inflammatory diseases
Terpene/ Origin Inflammatory disease or Mechanism of action Reference (s)
terpenoid experimental model
Ginkgolide C Ginkgo biloba leaves I/R- related inflammation Suppression of CD40-NF-κB signal pathway; 229,230
inhibition of downstream inflammatory cytokines,
IKK-β, and IκB-α phosphorylation
α-Pinene Oils of coniferous trees LPS-induced macrophages Inhibition of MAPK, NF-κB, and pro-inflammatory 231,232
and rosemary cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-α
Linalool Essential oils of Cigarette smoke-induced Inhibition of NF-κB activation; inhibition of 231,226,233,234
aromatic plants acute lung inflammation; pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6,
LPS-induced inflammation in IL-1β, IL-8, and MCP-1)
microglial cells
p-Cymene N/A Elastase-induced lung Inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, such as 231,235
emphysema and inflammation IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-17, in BALF
Malloconspur A Mallotus conspurcatus Pelvic inflammatory N/A 236
and malloconspur croizat (Euphorbiaceae) disease and possibly other
B (diterpenoids) (Native to China) inflammatory diseases
α-Pinene Essential oils of Skin inflammation Photoprotective effect against inflammatory 232,237
coniferous trees signaling in human skin cells; inhibition of
UVA-induced expression of inflammatory protein,
such as TNF-α and IL-6; suppression of MAPKs
pathway through inhibition of ERK and JNK
phosphorylation
β-Pinene Boswellia serrata Linn. RA Inhibition of inflammatory biomarkers (NF-κB, 222
COX-2, and LOX-5) involved in the pathogenesis
of RA
D-Limonene Essential oils of citrus Neuroinflammation Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1, 219,234,238
plants IL-6, and TNF-α
Abbreviations: BLAF: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; I/R: Ischemia/reperfusion; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase;
MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; N/A: Not available; RA: Rheumatoid arthritis.
TNF-α. 197,228 Moreover, linalool, myrcene, carvacrol, glutamate, a pro-inflammatory amino acid. 182,197 Table 5
α-phellandrene, paeoniflorin, and citronellal reportedly displays the mechanisms of action of several common
downregulated GluN2B receptors and, subsequently, terpenes (and terpenoids) as anti-inflammatory agents.
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 7 doi: 10.36922/itps.0332