Page 18 - ITPS-7-3
P. 18
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Therapeutic value of terpenes
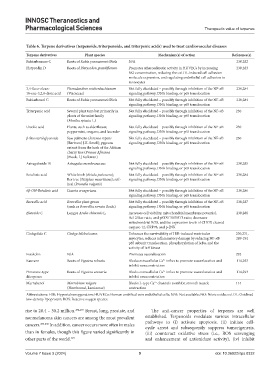
Table 6. Terpene derivatives (terpenoids, triterpenoids, and triterpenic acids) used to treat cardiovascular diseases
Terpene derivatives Plant species Mechanism(s) of action Reference(s)
Rubiarbonone C Roots of Rubia yunnanensis Diels N/A 230,282
Platycodin D Roots of Platycodon grandiflorum Promotes atherosclerotic activity in HUVECs by increasing 230,283
NO concentration, reducing the oxLDL-induced cell adhesion
molecule expression, and regulating endothelial cell adhesion to
monocytes
3,4-Seco-olean- Phoradendron reichenbachianum Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,284
18-ene-3,2,8-dioic acid (Viscaceae) signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
Rubiarbonol C Roots of Rubia yunnanensis Diels Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,284
signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
Triterpenic acid Several plant taxa but primarily in Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230
plants of the mint family signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
(Mentha spicata L.)
Ursolic acid Plants, such as elderflower, Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230
peppermint, oregano, and lavender signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
β-Sitosterol glycoside Saw palmetto (Serenoa repens Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230
[Bartram] J.K. Small); pygeum signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
extract from the bark of the African
cherry tree (Prunus Africana
[Hook. f.] Kalkman)
Astragaloside IV Astragalus membranaceus Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,285
signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
Betulinic acid White birch (Betula pubescens); Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,284
Ber tree (Ziziphus mauritiana); self- signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
heal (Prunella vulgaris)
6β-OH-Betulinic acid Licania cruegeriana Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,286
signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
Boswellic acid Boswellia plant genus Not fully elucidated – possibly through inhibition of the NF-κB 230,287
(such as Boswellia serrata Roxb.) signaling pathway, DNA binding, or p65 translocation
Elatoside C Longya Aralia chinensis L. Increases cell viability, mitochondrial membrane potential, 230,288
Bcl-2/Bax ratio, and pSTAT3/STAT3 ratio; decreases
mitochondrial ROS, and the expression levels of CHOP, cleaved
caspase-12, GRP78, and p-JNK
Ginkgolide C Ginkgo biloba leaves Enhances the survivability of H/R-induced ventricular 230,231,
myocytes; reduces inflammatory damage by reducing NF-κB 289-291
p65 subunit translocation, phosphorylation of IκBα, and the
activity of IκB kinase
Forskolin N/A Promotes vasorelaxation 292
Kaurane Roots of Viguiera robusta Blocks extracellular Ca influx to promote vasorelaxation and 114,293
2+
inhibit vasoconstriction
Pimarane-type Roots of Viguiera arenaria Blocks extracellular Ca influx to promote vasorelaxation and 114,293
2+
diterpenes inhibit vasoconstriction
Marrubenol Marrubium vulgare Blocks L-type Ca channels to inhibit smooth muscle 114
2+
(Horehound, Lamiaceae) contraction
Abbreviations: H/R: Hypoxia/reoxygenation; HUVECs: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; N/A: Not available; NO: Nitric oxide; oxLDL: Oxidized
low-density lipoprotein; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
rise to 28.4 – 30.2 million. 294,297 Breast, lung, prostate, and The anti-cancer properties of terpenes are well
nonmelanoma skin cancers are among the most prevalent established. Terpenoids modulate various intracellular
cancers. 294,296 In addition, cancer occurs more often in males pathways to (i) activate apoptosis, (ii) initiate cell-
cycle arrest and subsequently suppress tumorigenesis,
than in females, though this figure varied significantly in (iii) counteract oxidative stress (i.e., ROS scavenging
other parts of the world. 294 and enhancement of antioxidant activity), (iv) inhibit
Volume 7 Issue 3 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/itps.0332