Page 102 - ITPS-8-1
P. 102
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences BDNF-AS biomarker in multiple sclerosis
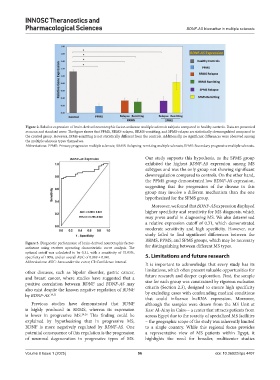
Figure 2. Relative expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-antisense multiple sclerosis subjects compared to healthy controls. Data are presented
as mean and standard error. The figure shows that PPMS, RRMS-relapse, RRMS-remitting, and SPMS-relapse are statistically downregulated compared to
the control group. However, SPMS-remitting is not statistically different from the controls. Additionally, no significant differences were observed among
the multiple sclerosis types themselves.
Abbreviations: PPMS: Primary progressive multiple sclerosis; RRMS: Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; SPMS: Secondary progressive multiple sclerosis.
Our study supports this hypothesis, as the SPMS group
exhibited the highest BDNF-AS expression among MS
subtypes and was the only group not showing significant
downregulation compared to controls. On the other hand,
the PPMS group demonstrated low BDNF-AS expression,
suggesting that the progression of the disease in this
group may involve a different mechanism than the one
hypothesized for the SPMS group.
Moreover, we found that BDNF-AS expression displayed
higher specificity and sensitivity for MS diagnosis, which
may prove useful in diagnosing MS. We also determined
a relative expression cutoff of 0.31, which demonstrated
moderate sensitivity and high specificity. However, our
study failed to find significant differences between the
RRMS, PPMS, and SPMS groups, which may be necessary
Figure 3. Diagnostic performance of brain-derived neurotrophic factor-
antisense using receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. The for distinguishing between different MS types.
optimal cutoff was calculated to be 0.31, with a sensitivity of 75.93%,
specificity of 100%, and an overall AUC of 0.869 ± 0.041. 5. Limitations and future research
Abbreviations: AUC: Area under the curve; CI: Confidence interval.
It is important to acknowledge that every study has its
other diseases, such as bipolar disorder, gastric cancer, limitations, which often present valuable opportunities for
and breast cancer, where studies have suggested that a future research and deeper exploration. First, the sample
positive correlation between BDNF and BDNF-AS may size for each group was constrained by rigorous exclusion
also exist despite the known negative regulation of BDNF criteria (Section 2.3), designed to ensure high specificity
by BDNF-AS. 19,31 by excluding cases with confounding medical conditions
that could influence lncRNA expression. Moreover,
Previous studies have demonstrated that BDNF although the samples were drawn from the MS Unit at
is highly produced in RRMS, whereas its expression Kasr Al-Ainy in Cairo – a center that attracts patients from
is lower in progressive MS. 24,26 This finding could be across Egypt due to the scarcity of specialized MS facilities
explained by hypothesizing that in progressive MS, – the geographic scope of the study was inherently limited
BDNF is more negatively regulated by BDNF-AS. One to a single country. While this regional focus provides
potential consequence of this regulation is the progression a representative view of MS patients within Egypt, it
of neuronal degeneration in progressive types of MS. highlights the need for broader, multicenter studies
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2025) 96 doi: 10.36922/itps.4407