Page 109 - ITPS-8-1
P. 109
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Steroids in septic cavernous thrombosis
of amitriptyline and planned for repeat MRV in 6 months
to assess resolution and remained on anticoagulation
therapy.
3. Discussion
The prevalence of SCST has markedly declined in the
antibiotic era, and its mortality rate has significantly
reduced to <30% in the postantibiotic era. However, it
remains potentially lethal with long-term complications.
3
The subtle nature of early symptoms frequently results
in delayed recognition and treatment initiation, causing
guarded prognostication in SCST. Magnetic resource
4
imaging (MRI) and MRV are the preferred imaging
modalities for diagnosing cerebral venous thrombosis
(CVT). Identifying CST complicating bacterial meningitis
3
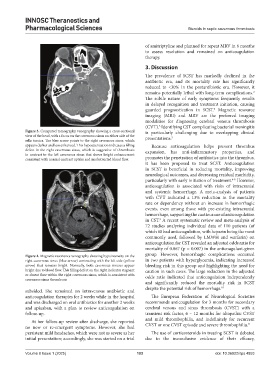
Figure 3. Computed tomography venography showing a cross-sectional is particularly challenging due to overlapping clinical
view of the head, with a focus on the cavernous sinus on either side of the presentations. 5
sella turcica. The blue arrow points to the right cavernous sinus, which
appears darker and less enhanced. This hypoattenuation indicates a filling Because anticoagulation helps prevent thrombus
defect in the right cavernous sinus, which is suggestive of thrombosis expansion, has anti-inflammatory properties, and
in contrast to the left cavernous sinus that shows bright enhancement
consistent with normal contrast uptake and unobstructed blood flow. promotes the penetration of antibiotics into the thrombus,
it has been proposed to treat SCST. Anticoagulation
in SCST is beneficial in reducing mortality, improving
neurological outcomes, and decreasing residual morbidity,
particularly with early initiation of treatment. However,
6-8
anticoagulation is associated with risks of intracranial
and systemic hemorrhage. A meta-analysis of patients
with CVT indicated a 13% reduction in the mortality
rate or dependency without an increase in hemorrhagic
events, even among those with pre-existing intracranial
hemorrhage, supporting the cautious use of anticoagulation
in CST. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of
9
72 studies analyzing individual data of 110 patients (of
which 60 had anticoagulation, with heparin being the most
commonly used, followed by LMWH and warfarin) on
anticoagulation for CST revealed an adjusted odds ratio for
mortality of 0.067 (p = 0.007) in the anticoagulant-given
Figure 4. Magnetic resonance venography showing hypointensity on the group. However, hemorrhagic complications occurred
right cavernous sinus (blue arrow) contrasting with the left side (yellow in two patients with hyperglycemia, indicating increased
arrow) that remains bright. Normally, both cavernous sinuses appear bleeding risk in this group and highlighting the need for
bright due to blood flow. This filling defect on the right indicates stagnant caution in such cases. The large reduction in the adjusted
or absent flow within the right cavernous sinus, which is consistent with odds ratio indicated that anticoagulation independently
cavernous sinus thrombosis
and significantly reduced the mortality risk in SCST
despite the potential risk of hemorrhage. 10
subsided. She remained on intravenous antibiotic and
anticoagulation therapies for 2 weeks while in the hospital The European Federation of Neurological Societies
and was discharged on oral antibiotics for another 2 weeks recommends anticoagulation for 3 months for secondary
and apixaban, with a plan to review anticoagulation on cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis (CVST) with a
follow-up. transient risk factor, 6 – 12 months for idiopathic CVST
At her follow-up review after discharge, she reported and mild thrombophilia, and indefinitely for recurrent
11
no new or re-emergent symptoms. However, she had CVST or one CVST episode and severe thrombophilia.
persistent mild headaches, which were not as severe as her The use of corticosteroids in treating SCST is debated
initial presentation; accordingly, she was started on a trial due to the inconclusive evidence of their efficacy,
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2025) 103 doi: 10.36922/itps.4853