Page 88 - ITPS-8-2
P. 88
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Antioxidant effects of curcumin in SCI
3.3.3. Casp-1 processes, are not yet fully understood. This knowledge
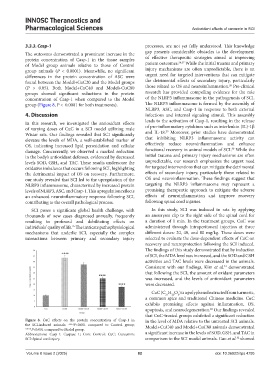
The outcomes demonstrated a prominent increase in the gap presents considerable obstacles to the development
protein concentration of Casp-1 in the tissue samples of effective therapeutic strategies aimed at improving
26,27
of Model group animals relative to those of Control patient outcomes. While the initial trauma and primary
group animals (P < 0.0001). Meanwhile, no significant injury mechanisms are often unpredictable, there is an
differences in the protein concentration of ASC were urgent need for targeted interventions that can mitigate
found between the Model+CuC20 and the Model groups the detrimental effects of secondary injury, particularly
28
(P > 0.05). Both Model+CuC40 and Model+CuC80 those related to OS and neuroinflammation. Pre-clinical
groups showed significant reductions in the protein research has provided compelling evidence for the role
concentration of Casp-1 when compared to the Model of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of SCI.
group (Figure 8, P < 0.0001 for both treatments). The NLRP3 inflammasome is formed by the assembly of
NLRP3, ASC, and Casp-1 in response to both external
4. Discussion infections and internal signaling stimuli. This assembly
In this research, we investigated the antioxidant effects leads to the activation of Casp-1, resulting in the release
of varying doses of CuC in a SCI model utilizing male of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-1β
29
Wistar rats. Our findings revealed that SCI significantly and IL-18. Moreover, prior studies have demonstrated
elevates the levels of MDA, a well-established marker of that inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activity can
OS, indicating increased lipid peroxidation and cellular effectively reduce neuroinflammation and enhance
30
damage. Concurrently, we observed a marked reduction functional recovery in animal models of SCI. While the
in the body’s antioxidant defenses, evidenced by decreased initial trauma and primary injury mechanisms are often
levels SOD, GSH, and TAC. These results underscore the unpredictable, our research emphasizes the urgent need
oxidative imbalance that occurs following SCI, highlighting for targeted interventions that can mitigate the detrimental
the detrimental impact of OS on recovery. Furthermore, effects of secondary injury, particularly those related to
our study revealed that SCI led to the upregulation of the OS and neuroinflammation. These findings suggest that
NLRP3 inflammasome, characterized by increased protein targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome may represent a
levels of NLRP3, ASC, and Casp-1. This upregulation reflects promising therapeutic approach to mitigate the adverse
an enhanced neuroinflammatory response following SCI, effects of neuroinflammation and improve recovery
contributing to the overall pathological process. following spinal cord injuries.
SCI poses a significant global health challenge, with In this study, SCI was induced in rats by applying
thousands of new cases diagnosed annually, frequently an aneurysm clip to the right side of the spinal cord for
resulting in profound and debilitating effects on a duration of 1 min. In the treatment groups, CuC was
individuals’ quality of life. The intricate pathophysiological administered through intraperitoneal injection at three
25
mechanisms that underlie SCI, especially the complex different doses: 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg. These doses were
interactions between primary and secondary injury selected to evaluate the dose-dependent effects of CuC on
recovery and neuroprotection following the SCI induced.
The findings of this study demonstrated that by induction
of SCI, the MDA level was increased, and the SOD and GSH
activities and TAC levels were decreased in the animals.
Consistent with our findings, Kim et al. demonstrated
31
that following the SCI, the amount of oxidant parameters
was increased, and the levels of antioxidant parameters
were decreased.
CuC (C H O ) is a polyphenol extracted from turmeric,
21
20
6
a common spice and traditional Chinese medicine. CuC
exhibits promising effects against inflammation, OS,
apoptosis, and neurodegeneration. Our findings revealed
22
that CuC-treated groups exhibited a significant reduction
Figure 8. CuC effects on the protein concentration of Casp-1 in in the level of MDA relative to the untreated SCI animals.
the SCI-induced animals. ++++ P<0.001 compared to Control group; Model+CuC40 and Model+CuC80 animals demonstrated
****P<0.001 compared to Model group.
Abbreviations: Casp-1: Caspase 1; Con: Control; CuC: Curcumin; a significant increase in the levels of SOD, GSH, and TAC in
32
SCI: Spinal cord injury. comparison to the SCI model animals. Gao et al. showed
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 82 doi: 10.36922/itps.4795