Page 50 - ITPS-8-3
P. 50
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Precision medicine and beyond in oncology
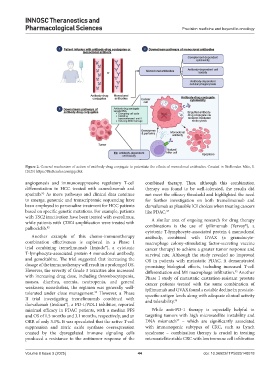
Figure 2. General mechanism of action of antibody-drug conjugate to potentiate the effects of monoclonal antibodies. Created in BioRender. Mito, S.
(2025) https://BioRender.com/gqcdtct.
angiogenesis and immunosuppressive regulatory T-cell combined therapy. Thus, although this combination
differentiation in HCC treated with camrelizumab and therapy was found to be well-tolerated, the results did
apatinib. As more pathways and clinical data continue not meet the efficacy threshold and highlighted the need
92
to emerge, genomic and transcriptomic sequencing have for further investigation on both tremelimumab and
been employed to personalize treatment for HCC patients durvalumab as plausible ICI choices when treating cancers
based on specific genetic mutations. For example, patients like PDAC. 94
with TSC2 inactivation have been treated with everolimus,
while patients with CDK4 amplification were treated with A similar area of ongoing research for drug therapy
palbociclib. 82 combinations is the use of ipilimumab (Yervoy®), a
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 monoclonal
Another example of this chemo-immunotherapy antibody, combined with GVAX (a granulocyte-
combination effectiveness is explored in a Phase I macrophage colony-stimulating factor-secreting vaccine
trial combining tremelimumab (Imjudo®), a cytotoxic cancer therapy) to achieve a greater tumor response and
T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 monoclonal antibody, survival rate. Although the study revealed no improved
and gemcitabine. The trial suggested that increasing the OS in patients with metastatic PDAC, it demonstrated
dosage of the immunotherapy will result in a prolonged OS. promising biological effects, including increased T-cell
However, the severity of Grade 3 toxicities also increased differentiation and M1 macrophage infiltration. Another
95
with increasing drug dose, including thrombocytopenia, Phase I study of metastatic castration-resistant prostate
nausea, diarrhea, anemia, neutropenia, and general cancer patients treated with the same combination of
weakness; nonetheless, the regimen was generally well- ipilimumab and GVAX found a notable decline in prostate-
tolerated under close management. However, a Phase specific antigen levels along with adequate clinical activity
93
II trial investigating tremelimumab combined with and tolerability. 96
durvalumab (Imfinzi®), a PD-1/PDL1 inhibitor, reported
minimal efficacy in PDAC patients, with a median PFS While anti-PD-1 therapy is especially helpful in
and OS of 1.5 months and 3.1 months, respectively, and an targeting tumors with high microsatellite instability and
ORR of only 3.1%. It was speculated that the active T-cell DNA mismatch – which are significantly associated
97
suppression and nitric oxide synthase overexpression with immunogenic subtypes of CRC, such as Lynch
created by the dysregulated immune signaling cells syndrome – combination therapy is crucial in treating
produced a resistance to the antitumor response of the microsatellite stable CRC with low immune cell infiltration
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 44 doi: 10.36922/ITPS025140018