Page 47 - ITPS-8-3
P. 47
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Precision medicine and beyond in oncology
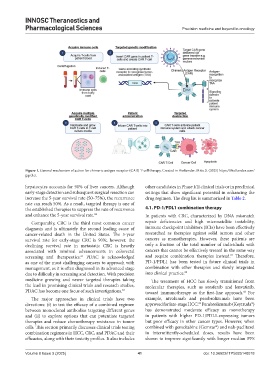
Figure 1. General mechanism of action for chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. Created in BioRender. Mito, S. (2025) https://BioRender.com/
gqcdtct.
hepatocytes accounts for 90% of liver cancers. Although other candidates in Phase I/II clinical trials or in preclinical
early-stage detection and subsequent surgical resection can settings that show significant potential in enhancing the
increase the 5-year survival rate (50–75%), the recurrence drug regimen. The drug list is summarized in Table 2.
rate can reach 50%. As a result, targeted therapy is one of
the established therapies to suppress the rate of recurrence 4.1. PD-1/PDL1 combination therapy
and enhance the 5-year survival rate. 62 In patients with CRC, characterized by DNA mismatch
Comparably, CRC is the third most common cancer repair deficiencies and high microsatellite instability,
diagnosis and is ultimately the second leading cause of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been effectively
cancer-related death in the United States. The 5-year researched as therapies against solid tumors and other
survival rate for early-stage CRC is 90%; however, the cancers as monotherapies. However, these patients are
declining survival rate in metastatic CRC is heavily only a fraction of the total number of individuals with
associated with minimal advancements in colorectal cancers that cannot be effectively treated in the same way
81
screening and therapeutics. PDAC is acknowledged and require combination therapies instead. Therefore,
63
as one of the most challenging cancers to approach with PD-1/PDL1 has been tested in future clinical trials in
management, as it is often diagnosed in its advanced stage combination with other therapies and slowly integrated
due to difficulty in screening and detection. With precision into clinical practice. 82
medicine growing and newer targeted therapies taking The treatment of HCC has slowly transitioned from
the lead in promising clinical trials and research studies, molecular therapies, such as sorafenib and lenvatinib,
PDAC has become one focus of such investigations. 64 toward immunotherapy as the first-line approach. For
83
The major approaches in clinical trials have two example, nivolumab and pembrolizumab have been
84
directions: (i) to test the efficacy of a combined regimen approved for late-stage HCC. Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®)
between monoclonal antibodies targeting different genes has demonstrated moderate efficacy as monotherapy
and (ii) to explore options that can potentiate targeted in patients with higher PD-1/PDL1-expressing tumors
therapies and reduce chemotherapy resistance in tumor but poor efficacy in other cancer types. However, when
cells. This section primarily discusses clinical trials testing combined with gemcitabine (Gemzar®) and nab-paclitaxel
combination regimens in HCC, CRC, and PDAC and their in intermittently-scheduled doses, results have been
efficacies, along with their toxicity profiles. It also includes shown to improve significantly with longer median PFS
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 41 doi: 10.36922/ITPS025140018