Page 46 - JCAU-6-3
P. 46
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Utilization of rural heritage
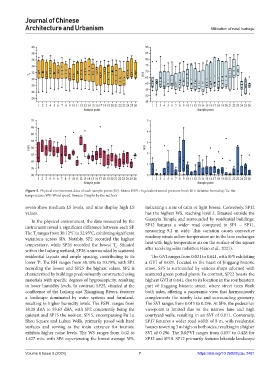
Figure 5. Physical environment data of each sample point (SP). Notes: ESPL: Equivalent sound pressure level; RH: Relative humidity; Ta: Air
temperature; WS: Wind speed. Source: Graphs by the authors
seven show medium LS levels, and nine display high LS indicating a state of calm or light breeze. Conversely, SP12
values. has the highest WS, reaching level 2. Situated outside the
In the physical environment, the data measured by the Guanyin Temple and surrounded by residential buildings,
instrument reveal a significant difference between each SP. SP12 features a wider road compared to SP1 – SP11,
The T ranges from 30.12°C to 32.93°C, exhibiting significant measuring 9.2 m wide. This variation causes convective
a
variations across SPs. Notably, SP2 recorded the highest roadway winds as low-temperature air in the lane exchanges
temperature, while SP26 recorded the lowest T. Situated heat with high-temperature air on the surface of the square
a
within the Lujiang wetland, SP26 is surrounded by scattered after receiving solar radiation (Guo et al., 2021).
residential layouts and ample spacing, contributing to its The GVI ranges from 0.021 to 0.641, with SP5 exhibiting
lower T. The RH ranges from 58.18% to 70.79%, with SP2 a GVI of 0.021. Located in the heart of Jinggang historic
a
recording the lowest and SP25 the highest values. SP2 is street, SP5 is surrounded by various shops adorned with
characterized by buildings predominantly constructed using scattered green potted plants. In contrast, SP22 boasts the
materials with specific degrees of hygroscopicity, resulting highest GVI at 0.641, due to its location in the southeastern
in lower humidity levels. In contrast, SP25, situated at the part of Jinggang historic street, where street trees flank
confluence of the Lujiang and Xiangjiang Rivers, features both sides, offering a panoramic view that harmoniously
a landscape dominated by water systems and farmland, complements the nearby lake and surrounding greenery.
resulting in higher humidity levels. The ESPL ranges from The SVI ranges from 0.011 to 0.296. At SP6, the pedestrian
38.28 dBA to 53.63 dBA, with SP2 consistently being the viewpoint is limited due to the narrow lane and high
quietest and SP15 the noisiest. SP15, encompassing Fu Lu courtyard walls, resulting in an SVI of 0.011. Conversely,
Shou Square and Luhua Wells, primarily paved with hard SP17 features a wider road width of 8 m, with residential
surfaces and serving as the main entrance for tourists, houses towering 3 m high on both sides, resulting in a higher
exhibits higher noise levels. The WS ranges from 0.02 to SVI of 0.296. The R&PVI ranges from 0.057 to 0.428 for
1.627 m/s, with SP6 experiencing the lowest average WS, SP12 and SP18. SP12 primarily features lakeside landscape
Volume 6 Issue 3 (2024) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.2481