Page 11 - JCBP-3-2
P. 11
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Theoretical models for test anxiety
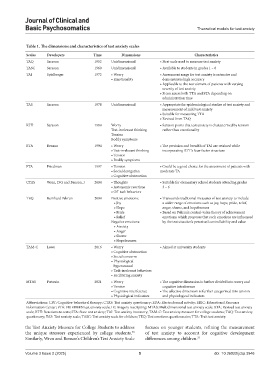
Table 1. The dimensions and characteristics of test anxiety scales
Scales Developers Time Dimensions Characteristics
TAQ Sarason 1952 Unidimensional • First scale used to measure test anxiety
TASC Sarason 1960 Unidimensional • Available to students in grades 1 – 6
TAI Spielberger 1972 • Worry • Assessment range for test anxiety is extensive and
• Emotionality demonstrates high accuracy
• Applicable to the recruitment of patients with varying
severity of test anxiety
• It can assess both TTA and STA depending on
administration time
TAS Sarason 1978 Unidimensional • Appropriate for epidemiological studies of test anxiety and
measurement of mild test anxiety
• Suitable for measuring TTA
• Revised from TAQ
RTT Sarason 1984 Worry • Sarason posits that test anxiety is characterized by tension
Test-irrelevant thinking rather than emotionality
Tension
Bodily symptoms
RTA Benson 1994 • Worry • The precision and breadth of TAI are retained while
• Test‑irrelevant thinking incorporating RTT’s four-factor structure
• Tension
• Bodily symptoms
FTA Friedman 1997 • Tension • Could be a good choice for the assessment of patients with
• Social derogation moderate TA
• Cognitive obstruction
CTAS Wren, D.G and Benson, J 2004 • Thoughts • Suitable for elementary school students attending grades
• Autonomic reactions 3 – 6
• Off‑task behaviors
TEQ Reinhard Pekrun 2004 Positive emotions: • Transcends traditional measures of test anxiety to include
• Joy a wider range of emotions such as joy, hope, pride, relief,
• Hope anger, shame, and hopelessness
• Pride • Based on Pekrun’s control‑value theory of achievement
• Relief emotions, which proposes that such emotions are influenced
Negative emotions: by the test situation’s perceived controllability and value
• Anxiety
• Anger
• Shame
• Hopelessness
TAM-C Lowe 2016 • Worry • Aimed at university students
• Cognitive obstruction
• Social concerns
• Physiological
hyperarousal
• Task‑irrelevant behaviors
• Facilitating anxiety
MTAS Putwain 2021 • Worry • The cognitive dimension is further divided into worry and
• Tension cognitive interference
• Cognitive interference • The affective dimension is further categorized into tension
• Physiological indicators and physiological indicators
Abbreviations: CBT: Cognitive-behavioral therapy; CTAS: Test anxiety questionary; EDA: Electrodermal activity; ERIC: Educational Resource
Information Center; FTA: FRIEDBEN test anxiety scale; IR: Imagery rescripting; MTAS: Multidimensional test anxiety scale; RTA: Revised test anxiety
scale; RTT: Reactions to tests; STA: State test anxiety; TAI: Test anxiety inventory; TAM-C: Test anxiety measure for college students; TAQ: Test anxiety
questionary; TAS: Test anxiety scale; TASC: Test anxiety scale for children; TEQ: Test emotions questionnaire; TTA: Trait test anxiety.
the Test Anxiety Measure for College Students to address focuses on younger students, refining the measurement
the unique stressors experienced by college students. of test anxiety to account for cognitive development
30
Similarly, Wren and Benson’s Children’s Test Anxiety Scale differences among children. 31
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.3946