Page 33 - JCTR-10-1
P. 33
Shah et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(1): 25-32 29
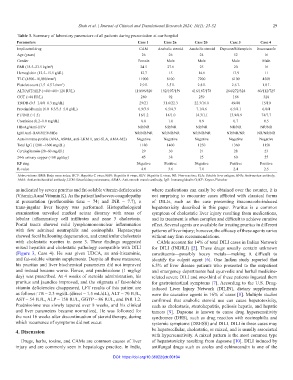
Table 3. Summary of laboratory parameters of all patients during presentation at our hospital
Parameters Case 1 Case 2a Case 2b Case 3 Case 4
Implicated drug CAM Anabolic steroid Anabolic steroid Dapsone/Rifampicin Itraconazole
Age (years) 26 26 24 52 16
Gender Female Male Male Male Male
BMI (18.5–23.5 kg/m ) 24.5 27.6 25 20 16
2
Hemoglobin (12.5–15.5 g/dL) 12.7 15 14.6 13.9 11
TLC (4500–10,000/mm ) 11000 8100 7200 6100 4500
3
Platelet count (1.5–4.5 L/mm ) 2.9 L 3.5 L 2.8 L 2.6 L 1.8 L
3
ALT/AST/ALP (<40/<40/<120 IU/L) 110/96/820 192/107/159 416/187/178 264/272/324 60/112/725
GGT (<40 IU/L) 280 92 259 168 320
TB/DB (0.3–1.0/0–0.3 mg/dL) 29/21 31.6/22.3 22.3/16.8 49/40 15/10
Protein/albumin (6.0–8.3/3.5–5.0 g/dL) 6.9/3.9 6.5/4.3 7.1/4.6 6.5/4.1 6.0/4
PT/INR (<1.5) 16/1.2 14/1.0 14.3/1.1 13.9/0.9 74/7.7
Creatinine (0.2–1.0 mg/dL) 0.8 1.0 0.9 0.7 0.5
HBsAg/Anti-HCV NR/NR NR/NR NR/NR NR/NR NR/NR
IgM Anti-HAV/HEV/HBc NR/NR/NR NR/NR/NR NR/NR/NR NR/NR/NR NR/NR/NR
Autoimmune profile (ANA, ASMA, anti-LKM 1, anti-SLA, AMA-M2) Negative Negative Negative Negative Negative
Total IgG (1200 –1600 mg/dL) 1180 1400 1250 1360 1150
Ceruloplasmin (20–60 mg/dL) 29 30 21 28 23
24-h urinary copper (<60 µg/day) 45 38 25 60 55
KF ring Negative Positive Negative Positive Positive
R-value 4.0 3.6 7.0 2.4 2.5
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HAV: Hepatitis A virus; HEV: Hepatitis E virus; NR: Non-reactive; SLA: Soluble liver antigen; ANA: Anti-nuclear antibody;
AMA: Anti-mitochondrial antibody; LKM: Liver kidney microsome; ASMA: Anti-smooth muscle antibody; IgG: Immunoglobulin G; KF: Kayser-Fleischer
as indicated by severe pruritus and fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies where medications can easily be obtained over the counter, it is
(Vitamin A and Vitamin K). As the patient had severe coagulopathy not surprising to encounter cases afflicted with classical forms
at presentation (prothrombin time – 74; and INR – 7.7), a of DILIs, such as the case presenting itraconazole-induced
trans-jugular liver biopsy was performed. Histopathological hepatotoxicity described in this paper. Pruritus is a common
examination unveiled marked acinar disarray with areas of symptom of cholestatic liver injury resulting from medications,
lobular inflammatory cell infiltrates and zone 3 cholestasis. and its treatment is often complex and difficult to achieve curative
Portal tracts showed mild lymphomononuclear inflammation effect. Several agents are available for treating pruritus in different
with few admixed neutrophils and eosinophils. Hepatocytes patterns of liver injury; however, the efficacy of these agents varies
showed focal ballooning degeneration, and canalicular cholestasis without any firm recommendations.
with cholestatic rosettes in zone 3. These findings suggested CAMs account for 14% of total DILI cases in Indian Network
mixed hepatitis and cholestatic pathology compatible with DILI for DILI (INDILI) [2]. These drugs usually contain unknown
(Figure 3, Case 4). He was given UDCA, an anti-histaminic, constituents—possibly heavy metals—making it difficult to
and fat-soluble vitamin supplements. Despite all these measures, identify the culprit agent [6]. One Indian study reported that
his pruritus and liver biochemical parameters did not improved 6.5% of liver disease patients who presented to the outpatient
and instead became worse. Hence, oral prednisolone (1 mg/kg/ and emergency departments had ayurvedic and herbal medicine-
day) was prescribed. At 4 weeks of steroids administration, his related severe DILI and one-third of these patients ingested them
pruritus and jaundice improved, and the stigmata of fat-soluble for gastrointestinal symptoms [7]. According to the U.S. Drug-
vitamin deficiencies disappeared. LFT results of this patient are induced Liver Injury Network (DILIN), dietary supplements
as follows: TB – 2.3 mg/dL (direct – 1.5 mL/dL), ALT – 70 IU/L, were the causative agents in 16% of cases [8]. Multiple studies
AST – 54 IU/L, ALP – 150 IU/L, GGTP – 86 IU/L, and INR 1.2. confirmed that anabolic steroid use can cause hepatotoxicity,
Prednisolone was slowly tapered over 8 weeks, and his clinical such as cholestasis, steatohepatitis, peliosis hepatis, and hepatic
and liver parameters became normalized. He was followed for tumors [9]. Dapsone is known to cause drug hypersensitivity
the next 16 weeks after discontinuation of steroid therapy, during syndromes (DHS), such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and
which recurrence of symptoms did not occur. systemic symptoms (DRESS) and DILI. DILI in these cases may
4. Discussion be hepatocellular, cholestatic, or mixed, and is usually associated
with hypersensitivity. A mixed pattern is the most common type
Drugs, herbs, toxins, and CAMs are common causes of liver of hepatotoxicity resulting from dapsone [10]. DILI induced by
injury and are commonly seen in hepatology practice. In India, antifungal drugs such as azoles and echinocandin is one of the
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.00104