Page 41 - JCTR-10-1
P. 41
Gonda et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(1): 33-51 37
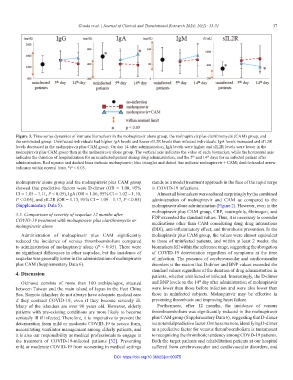
Figure 3. Time-series dynamics of immune biomarkers in the molnupiravir alone group, the molnupiravir plus clarithromycin (CAM) group, and
the uninfected group. Uninfected individuals had higher IgA levels and lower sIL2R levels than infected individuals. IgA levels increased and sIL2R
levels decreased in the molnupiravir plus CAM group. On day 14 after administration, IgA levels were higher and sIL2R levels were lower in the
molnupiravir plus CAM group than in the molnupiravir alone group. The vertical axis indicates the value of each biomarker, while the horizontal axis
indicates the duration of hospitalization for an uninfected patient during drug administration, and the 5 and 14 days for an infected patient after
th
th
administration. Red squares and dashed lines indicate molnupiravir; blue triangles and dotted line indicate molnupiravir + CAM; double-headed arrow
indicates within normal limit. *P < 0.05.
molnupiravir alone group and the molnupiravir plus CAM group stands as a model treatment approach in the face of the rapid surge
showed that predictive factors were D-dimer (OR = 1.08, 95% in COVID-19 infections.
CI = 1.05 – 1.11, P < 0.05), IgA (OR = 1.06, 95% CI = 1.02 – 1.10, Almost all biomarkers were reduced surprisingly by the combined
P < 0.05), and sIL2R (OR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.09 – 1.17, P < 0.05) administration of molnupiravir and CAM as compared to the
(Supplementary Data 5). molnupiravir alone administration (Figure 2). However, even in the
molnupiravir plus CAM group, CRP, neutrophils, fibrinogen, and
3.5. Comparison of severity of sequelae 12 months after FDP exceeded the standard values. Thus, it is necessary to consider
COVID-19 treatment with molnupiravir plus clarithromycin or
molnupiravir alone medications other than CAM considering drug–drug interactions
(DDI), anti-inflammatory effect, and thrombosis prevention. In the
Administration of molnupiravir plus CAM significantly molnupiravir plus CAM group, the values were almost equivalent
reduced the incidence of venous thromboembolism compared to those of uninfected patients, and within at least 2 weeks, the
to administration of molnupiravir alone (P < 0.05). There were biomarkers fell within the reference range, suggesting the abrogation
no significant differences in other sequelae, but the incidence of of COVID-19 deterioration regardless of symptoms at the time
sequelae was generally lower in the administration of molnupiravir of infection. The presence of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular
plus CAM (Supplementary Data 6). disorders is the reason that D-dimer and BNP values exceeded the
standard values regardless of the duration of drug administration in
4. Discussion patients, whether uninfected or infected. Interestingly, the D-dimer
th
Okinawa consists of more than 160 archipelagos, situated and BNP levels on the 14 day after administration of molnupiravir
between Taiwan and the main island of Japan in the East China were lower than those before infection and were also lower than
Sea. Remote islanders do not always have adequate medical care those in uninfected subjects. Molnupiravir may be effective in
if they contract COVID-19, even if they become severely ill. preventing thrombosis and improving heart failure.
Many of the islanders are over 90 years old. However, elderly Furthermore, after 12 months, the incidence of venous
patients with pre-existing conditions are more likely to become thromboembolism was significantly reduced in the molnupiravir
seriously ill if infected. Therefore, it is imperative to prevent the plus CAM group (Supplementary Data 6), suggesting that D-dimer
deterioration from mild or moderate COVID-19 to severe form, is a potential predictive factor. On the same note, identifying D-dimer
necessitating ventilator management among elderly patients, and as a predictive factor for venous thromboembolism is tantamount
it is also our responsibility as medical professionals to engage in to recognizing the thrombotic tendency among COVD-19 patients.
the treatment of COVID-19-infected patients [32]. Preventing Both the target patients and rehabilitation patients at our hospital
mild or moderate COVID-19 from worsening in medical settings suffered from cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disorders, and
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.00075