Page 12 - JCTR-10-4
P. 12
234 Tyson et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(4): 229-236
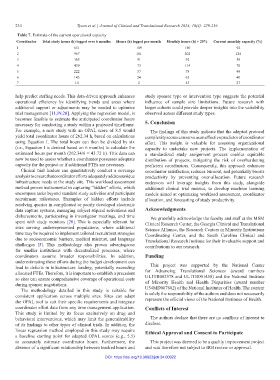
Table 7. Estimate of the current operational capacity
Coordinator Total study hours (h) logged over 6 months Hours (h) logged per month Monthly hours (h) + 25% Current monthly capacity (%)
1 651 109 150 92
2 967 161 202 124
3 305 51 92 56
4 439 73 114 70
5 222 37 78 48
6 145 24 65 40
7 14 2 43 27
help predict staffing needs. This data-driven approach enhances study sponsor type or intervention type suggests the potential
operational efficiency by identifying trends and areas where influence of sample size limitations. Future research with
additional support or adjustments may be needed to optimize larger cohorts could provide deeper insights into the variability
trial management [11,19,20]. Applying the regression model, it observed across different study types.
becomes feasible to estimate the anticipated coordinator hours
necessary for conducting a study within a projected timeframe. 5. Conclusion
For example, a new study with an OPAL score of 8.5 would The findings of this study indicate that the adapted protocol
yield total coordinator hours of 262.34 h, based on calculations complexity scores can serve as an effective predictor of coordinator
using Equation I. The total hours can then be divided by six effort. This insight is valuable for assessing organizational
(i.e., Equation I is derived based on 6 months) to calculate the capacity to undertake new projects. The implementation of
estimated hours per month (262.34/6 = 43.72 h). This data can a standardized study assignment process enables equitable
now be used to assess whether a coordinator possesses adequate distribution of projects, mitigating the risk of overburdening
capacity for the project or if additional FTEs are necessary. proficient coordinators. Consequently, this approach enhances
Clinical trial leaders can quantitatively conduct a coverage coordinator satisfaction, reduces burnout, and potentially boosts
analysis to ensure that coordinator efforts adequately address unique productivity by preventing over-allocation. Future research
infrastructure needs at the study site. This workload assessment endeavors will leverage insights from this study, alongside
method proves instrumental in capturing “hidden” efforts, which additional clinical trial metrics, to develop machine learning
encompass tasks beyond standard study activities and participant models aimed at optimizing workload assessment, coordinator
recruitment milestones. Examples of hidden efforts include allocation, and forecasting of study productivity.
resolving queries in complicated or poorly developed electronic
data capture systems, managing subject stipend activations and Acknowledgments
disbursements, participating in investigator meetings, and time We gratefully acknowledge the faculty and staff at the MSM
spent with study monitors [28]. This is especially relevant for Clinical Research Center, the Georgia Clinical and Translational
sites serving underrepresented populations, where additional Science Alliance, the Research Centers in Minority Institutions
time may be required to implement tailored recruitment strategies Coordinating Center, and the South Carolina Clinical and
due to socioeconomic barriers, medical mistrust, and language Translational Research Institute for their invaluable support and
challenges [5]. This methodology also proves advantageous contributions to our research.
for smaller institutions with decentralized processes, where
coordinators assume broader responsibilities. In addition, Funding
underestimating these efforts during the budget development can
lead to deficits in infrastructure funding, potentially exceeding This project was supported by the National Center
allocated FTEs. Therefore, it is important to establish a precedent for Advancing Translational Sciences (award numbers
so sites can ensure comprehensive coverage of operational costs UL1TR002378 and UL1TR001450) and the National Institute
during sponsor negotiations. of Minority Health and Health Disparities (award number
The methodology detailed in this study is suitable for U54MD007602) of the National Institutes of Health. The content
consistent application across multiple sites. Sites can adapt is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily
represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
the OPAL tool to suit their specific requirements and integrate
coordinator effort data from any time management application. Conflicts of Interest
This study is limited by its focus exclusively on drug and
behavioral interventions, which may limit the generalizability The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest to
of its findings to other types of clinical trials. In addition, the disclose.
linear regression method employed in this study may require Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
a baseline starting point for adapted OPAL scores (e.g., 5.5)
to accurately estimate coordinator hours. Furthermore, the This project was deemed to be a quality improvement project
absence of a significant relationship between tracked hours and and was therefore not subject to IRB review or approval.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00022