Page 18 - JCTR-10-4
P. 18
240 de Almeida et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(4): 237-245
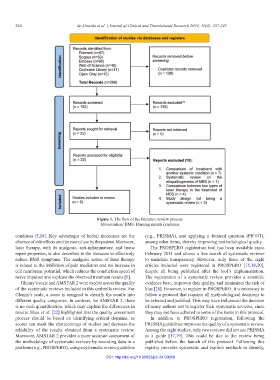
Figure 1. The flow of the literature review process
Abbreviation: BMS: Burning mouth syndrome
condition [5,18]. Key advantages of herbal medicines are the (e.g., PRISMA), and applying a focused question (PICOT),
absence of side effects and the ease of use by the patient. Moreover, among other items, thereby improving methodological quality.
laser therapy, with its analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and tissue The PROSPERO registration tool has been available since
repair properties, is also described in the literature to effectively February 2011 and allows a free search of systematic reviews
reduce BMS symptoms. The analgesic action of laser therapy to maintain transparency. However, only three of the eight
is related to the inhibition of pain mediators and the increase in articles included were registered in PROSPERO [15,18,20],
cell membrane potential, which reduces the conduction speed of despite all being published after the tool’s implementation.
nerve impulses and explains the observed treatment results [5]. The registration of a systematic review provides a scientific
Glenny’s scale and AMSTAR 2 were used to assess the quality evidence base, improves data quality, and minimizes the risk of
of the systematic reviews included in this umbrella review. For bias [28]. However, to register in PROSPERO, it is necessary to
Glenny’s scale, a score is assigned to classify the results into follow a protocol that requires all methodological decisions to
different quality categories. In contrast, for AMSTAR 2, there be selected and justified. This may have influenced the decision
is no such quantification, which may explain the differences in of many authors not to register their systematic reviews, since
results. Shea et al. [22] highlighted that the quality assessment they may not have adhered to some of the items in this protocol.
process should be based on identifying critical domains, as In addition to PROSPERO registration, following the
scores can mask the shortcomings of studies and decrease the PRISMA guidelines improves the quality of a systematic review.
reliability of the results obtained from a systematic review. Among the eight studies, only two reviews did not use PRISMA
Moreover, AMSTAR 2 provides a more accurate assessment of as a guide [17,19]. This could be due to the review being
the methodology of systematic reviews by recording data in a published before the launch of this protocol. Following this
platform (e.g., PROSPERO), using a systematic review guideline registry provides systematic and explicit methods to identify,
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00018