Page 19 - JCTR-10-4
P. 19
de Almeida et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(4): 237-245 241
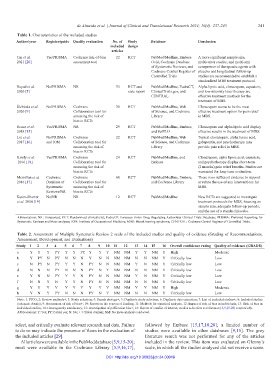
Table 1. Characteristics of the included studies
Author/year Register/guide Quality evaluation No. of Study Database Conclusion
included design
articles
Tan et al. Yes/PRISMA Cochrane risk-of-bias 22 RCT PubMed/Medline, Embase A more significant sample size,
2021 [20] assessment tool Ovid, Cochrane Database multicenter studies, and multi-arm
of Systematic Reviews, and comparison of therapeutic agents with
Cochrane Central Register of placebo and longitudinal follow-up
Controlled Trials studies are recommended to establish a
standardized MBS treatment protocol.
Reyad et al. No/PRISMA NR 53 RCT and PubMed/Medline, EudraCT, Alpha lipoic acid, clonazepam, capsaicin,
2020 [5] case report ClinicalTrials.gov, and and low-intensity laser therapy are
CENTRAL effective treatment methods for the
treatment of MBS.
Ślebioda et al. No/PRISMA Cochrane 30 RCT PubMed/Medline, Web Clonazepam seems to be the most
2020 [9] Collaboration tool for of Science, and Cochrane effective treatment option for pain relief
assessing the risk of Library in MBS.
bias in RCTs
Souza et al. Yes/PRISMA NR 29 RCT PubMed/Medline, Embase, Clonazepam and alpha lipoic acid display
2018 [15] and SciELO effective results in the treatment of MBS.
Liu et al. No/PRISMA Cochrane 22 RCT PubMed/Medline, Web Topical clonazepam, alpha lipoic acid,
2017 [16] and IOM Collaboration tool for of Science, and Cochrane gabapentin, and psychotherapy may
assessing the risk of Library provide pain relief in MBS.
bias in RCTs
Kisely et al. Yes/PRISMA Cochrane 24 RCT PubMed/Medline, and Clonazepam, alpha lipoic acid, capsaicin,
2016 [18] Collaboration tool for Embase and psychotherapy display short-term
assessing the risk of (2 months) pain relief benefits. Studies are
bias in RCTs warranted for long-term evaluation.
Mcmillan et al. Cochrane Cochrane 60 RCT PubMed/Medline, Embase, There is no sufficient evidence to support
2016 [17] Database of Collaboration tool for and Cochrane Library or refute the use of any interventions for
Systematic assessing the risk of MBS.
Reviews/NR bias in RCTs
Kuten-Shorrer No/NR NR 12 RCT PubMed/Medline New RCTs are suggested to investigate
et al. 2014 [19] treatment protocols for MBS, focusing on
sample size, adequate follow-up periods,
and the use of a standard placebo.
Abbreviations: NR: Unreported; RCT: Randomized clinical trial; EudraCT: European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials Database; PRISMA: Preferred Reporting for
Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses; IOM: Institute of Occupational Medicine; MBS: Mouth burning syndrome; CENTRAL: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials.
Table 2. Assessment of Multiple Systematic Review 2 scale of the included studies and quality of evidence (Grading of Recommendations,
Assessment, Development, and Evaluations)
Study 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Overall confidence rating Quality of evidence (GRADE)
a Y Y Y PY Y Y PY Y Y Y NM NM Y Y NM Y High Moderate
b Y PY N PY N N N Y N N NM NM N N NM Y Critically low Low
c N PY N PY Y Y N PY N N NM NM Y N NM Y Critically low Low
d N N N PY N N N PY N Y NM NM N N NM Y Critically low Low
e Y N N PY Y Y N PY N N NM NM Y N NM Y Critically low Low
f N N Y N Y Y N PY N N NM NM N N NM Y Critically low Low
g Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y NM NM Y Y NM Y High Moderate
h Y N Y PY N N N PY N Y NM NM N N NM Y Critically low Low
Note: 1: PICO; 2: Review methods+; 3: Study selection; 4: Search strategy+; 5: Duplicate study selection; 6: Duplicate data extraction; 7: List of excluded studies+; 8: Included studies
(adequate details); 9: Assessment of risk of bias+; 10: Report on the sources of funding; 11: Methods for statistical analysis; 12: Impact of risk of bias in individuals; 13: Risk of bias in
individual studies; 14: Heterogeneity satisfactory; 15: Investigation of publication bias+; 16: Report of conflict of interest; studies a–h refers to references [5,9,15-20] respectively.
Abbreviations: Y: Yes; PY: Partial yes; N: No; +: Critical domain; NM: No meta-analysis conducted.
select, and critically evaluate relevant research and data. Failure followed by Embase [15,17,18,20]; a limited number of
to do so may indicate the presence of flaws in the evaluation of studies were available in other databases [9,15]. The grey
the included articles [29]. literature search was not performed for any of the articles
All articles were available in the PubMed database [5,9,15-20]; included in the review. This item was evaluated on Glenny’s
most were available in the Cochrane Library [5,9,16,17], scale, in which all the studies analyzed did not receive a score.
DOI: http://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00018