Page 49 - JCTR-11-3
P. 49
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Greek propolis use in COVID-19: Trial protocol
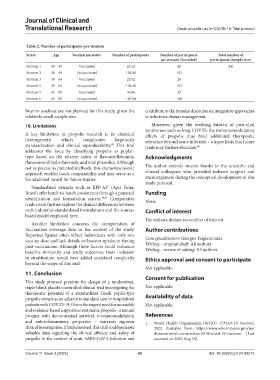
Table 2. Number of participants per stratum
Strata Age Vaccination status Number of participants Number of participants Total number of
per stratum (Rounded) participants (Sample size)
Stratum 1 18 – 49 Vaccinated 25.52 26 441
Stratum 2 18 – 49 Unvaccinated 102.08 102
Stratum 3 50 – 64 Vaccinated 25.52 26
Stratum 4 50 – 64 Unvaccinated 102.08 102
Stratum 5 65 – 85 Vaccinated 36.96 37
Stratum 6 65 – 85 Unvaccinated 147.84 148
Interim analyses are not planned for this study, given the contribute to the broader discourse on integrative approaches
relatively small sample size. to infectious disease management.
10. Limitations Moreover, given the evolving burden of post-viral
syndromes such as long COVID, the immunomodulatory
A key limitation in propolis research is its chemical effects of propolis may hold additional therapeutic
heterogeneity, which complicates large-scale relevance beyond acute infection – a hypothesis that future
standardization and clinical reproducibility. This trial trials may further elucidate. 80
60
addresses the issue by classifying propolis as poplar-
type based on the relative ratios of flavones/flavonols, Acknowledgments
flavanones/dihydroflavonols, and total phenolics. Although
not as precise as patented methods, this chemotaxonomic The author extends sincere thanks to the scientific and
approach enables batch comparability and may serve as a clinical colleagues who provided indirect support and
foundational model for future studies. encouragement during the conceptual development of this
study protocol.
®
Standardized extracts such as EPP-AF (Apis Flora,
Brazil) offer batch-to-batch consistency through a patented Funding
identification and formulation system. 78,79 Comparative None.
trials could further explore the clinical differences between
such industrial-standardized formulations and the source- Conflict of interest
based model employed here.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Another limitation concerns the interpretation of
vaccination coverage data in the context of the study. Author contributions
Reported figures often reflect individuals with only one
vaccine dose and lack details on booster uptake or timing Conceptualization: Giorgos Tzigkounakis
post-vaccination. Although these factors could influence Writing – original draft: All authors
baseline immunity and study outcomes, their inclusion Writing – review & editing: All authors
in stratification would have added analytical complexity Ethics approval and consent to participate
beyond the scope of this trial.
Not applicable.
11. Conclusion
This study protocol presents the design of a randomized, Consent for publication
triple-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial investigating the Not applicable.
therapeutic potential of a standardized Greek poplar-type
propolis extract as an adjunct to standard care in hospitalized Availability of data
patients with COVID-19. Given the urgent need for accessible Not applicable.
and evidence-based supportive treatments, propolis – a natural
product with demonstrated antiviral, immunomodulatory, References
and anti-inflammatory properties – warrants rigorous 1. World Health Organisation (WHO). COVID-19 Vaccines;
clinical investigation. If implemented, this trial could generate 2022. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/
valuable data regarding the clinical efficacy and safety of diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/covid-19-vaccines [Last
propolis in the context of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and accessed on 2022 Aug 18].
Volume 11 Issue 3 (2025) 43 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00073