Page 108 - JCTR-11-5
P. 108
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Uric acid, CTGF genotype, and prostate cancer
observations, we propose a new hypothesis: the impact of release and reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation,
uric acid on prostate cancer may be modulated by CTGF which in turn converts latent TGF-β to its active form.
genotype. In men homozygous for the CTGF common Active TGF-β signals through SMAD2/3 to induce
allele (C), uric acid may act as a pro-inflammatory agent, CTGF (CCN2) transcription. 30,31 CTGF is a matricellular
potentially increasing the risk of prostate cancer. In factor that strongly induces fibroblast activation (cancer-
contrast, among carriers of the CTGF minor allele (T), uric associated fibroblast, CAF) and ECM deposition and has
32
acid may exert antioxidative effects, serving as a protective been implicated in promoting tumor angiogenesis. These
factor, or have no significant impact on prostate cancer stromal changes create a reactive tumor microenvironment
risk. Antioxidants that can react with molecular oxygen (with CAFs, dense ECM, and new vessels) that fosters
and are reducing agents can act as prooxidants in the event prostate cancer cell motility and metastatic spread.
that they become overloaded. CTGF plays an integral part in maintaining stem cell
34
33
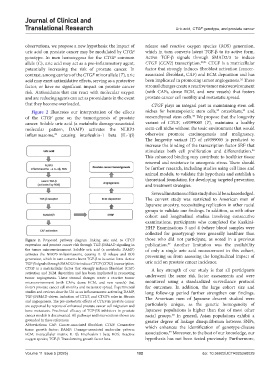
Figure 2 illustrates our interpretation of the effects niches for hematopoietic stem cells, osteoblasts, and
35
of the CTGF gene on the tumorigenesis of prostate mesenchymal stem cells. We propose that the longevity
cancer. Soluble uric acid (a metabolic damage-associated variant of CTGF, rs9399005 (T), maintains a healthy
molecular pattern, DAMP) activates the NLRP3 stem-cell niche without the toxic environment that would
29
inflammasome, causing interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) otherwise promote carcinogenesis and malignancy.
The longevity variant (T) of rs9399005 is predicted to
increase the binding of the transcription factor SRF that
stimulates both cell proliferation and differentiation.
36
This enhanced binding may contribute to healthier tissue
renewal and resistance to oncogenic stress. There should
be further research, including studies using cell lines and
animal models, to validate this hypothesis and establish a
theoretical foundation for developing targeted prevention
and treatment strategies.
Several limitations of this study should be acknowledged.
The current study was restricted to American men of
Japanese ancestry, necessitating replication in other racial
groups to validate our findings. In addition, as with other
cohort and longitudinal studies involving consecutive
examinations, participants who completed the Kuakini-
HHP Examinations 3 and 4 (where blood samples were
collected for genotyping) were generally healthier than
Figure 2. Proposed pathway diagram linking uric acid to CTGF those who did not participate, as noted in a previous
37
expression and prostate cancer risk through TGF-β/SMAD signaling in publication. Another limitation was the availability
the tumor microenvironment. Soluble uric acid (a metabolic DAMP) of only a single uric acid measurement in this cohort,
activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, causing IL-1β release and ROS preventing us from assessing the longitudinal impact of
generation, which in turn converts latent TGF-β to its active form. Active
TGF-β signals through SMAD2/3 to induce CTGF (CCN2) transcription. uric acid on prostate cancer incidence.
CTGF is a matricellular factor that strongly induces fibroblast (CAF) A key strength of our study is that all participants
activation and ECM deposition and has been implicated in promoting underwent the same risk factor assessments and were
tumor angiogenesis. These stromal changes create a reactive tumor
microenvironment (with CAFs, dense ECM, and new vessels) that monitored using a standardized surveillance protocol
fosters prostate cancer cell motility and metastatic spread. Experimental for outcomes. In addition, the large cohort size and
studies and reviews describe UA as an inflammasome-activating DAMP, long follow-up period further strengthen our findings.
TGF-β/SMAD-driven induction of CTGF, and CTGF’s roles in fibrosis The American men of Japanese descent studied were
and angiogenesis. The pro-metastatic effects of CTGF in prostate cancer
are supported by reports of enhanced prostate cancer cell migration and particularly unique, as the genetic homogeneity of
bone metastasis. Preclinical efficacy of TGF-βR inhibitors in prostate Japanese populations is higher than that of most other
38
cancer models is documented. All pathways and interventions shown are racial groups. In general, Asian populations exhibit a
grounded in these references. greater degree of linkage disequilibrium between SNPs,
Abbreviations: CAF: Cancer-associated fibroblast; CTGF: Connective which enhances the identification of genotype-disease
tissue growth factor; DAMP: Damage-associated molecular pattern; 39
ECM: Extracellular matrix; IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta; ROS: Reactive associations. Moreover, to the best of our knowledge, our
oxygen species; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta. hypothesis has not been tested previously. Furthermore,
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 102 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025260029